|
RNTI
RNTI stands for Radio Network Temporary Identifier. This is exactly same concept as LTE RNTI. So I would suggest you to read LTE RNTI part first and get the general understandings on how this works.
In short, you can think of RNTI is the CRC mask that is required to decode DCI message. Each of the DCI needs its own specific RNTI for UE to decode it. There are some common RNTI that is shared by every UE (e.g, SI-RNTI, P-RNTI etc), but most of the DCI requires a specific RNTI that is assigned to a specific UE.
Is there any specific RNTI values for a specific UE and Specific DCI type?
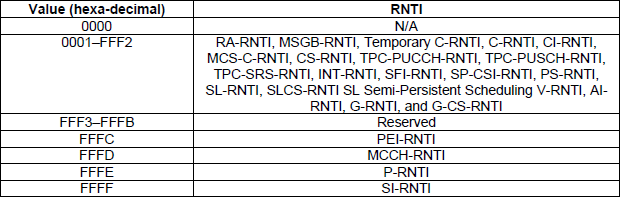
Some DCI uses (is masked by) a specific predefined RNTI that is common to every UE. SI-RNTI, P-RNTI, MCCH-RNTI, PEI-RNTI belong to this category.
All other types of DCI uses (is masked by) a RNTI that is assigned to a specific individual UE or a specific group of UEs
< 38.321 v17.1 - Table 7.1-1: RNTI values. >
< 38.321 v17.1 - Table 7.1-2: RNTI usage.. >
|
RNTI
|
Usage
|
Transport Channel
|
Logical Channel
|
|
P-RNTI
|
Paging and System Information change notification
|
PCH
|
PCCH
|
|
SI-RNTI
|
Broadcast of System Information
|
DL-SCH
|
BCCH
|
|
RA-RNTI
|
Random Access Response
|
DL-SCH
|
N/A
|
|
MSG-B-RNTI
|
Random Access Response for 2-step RA type
|
DL-SCH
|
N/A
|
|
Temporary C-RNTI
|
Contention Resolution (when no valid C-RNTI is allocated)
|
DL-SCH
|
CCCH, DCCH
|
|
Temporary C-RNTI
|
Msg3 transmission
|
UL-SCH
|
CCCH, DCCH, DTCH
|
|
C-RNTI, MCS-C-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled unicast transmission
|
UL-SCH
|
N/A
|
|
C-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled unicast transmission
|
DL-SCH
|
CCCH, DCCH, DTCH
|
|
MCS-C-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled unicast transmission
|
DL-SCH
|
DCCH, DTCH
|
|
C-RNTI
|
Triggering of PDCCH ordered random access
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
C-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled PTP retransmission for initial PTM transmission for multicast MBS
|
DL-SCH
|
MTCH
|
|
CS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled unicast transmission (activation, reactivation and retransmission)
|
DL-SCH, UL-SCH
|
DCCH, DTCH
|
|
CS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled unicast transmission (deactivation)
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
CS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled unicast transmission (PTP retransmission for initial PTM transmission)
|
DL-SCH
|
MTCH
|
|
CS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled unicast transmission (MBS SPS deactivation)
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
G-CS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled multicast transmission (activation, reactivation and retransmission)
|
DL-SCH
|
MTCH
|
|
G-CS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled multicast transmission (deactivation)
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
TPC-PUCCH-RNTI
|
PUCCH power control
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
TPC-PUSCH-RNTI
|
PUSCH power control
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
TPC-SRS-RNTI
|
SRS trigger and power control
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
INT-RNTI
|
Indication pre-emption in DL
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
SF1-RNTI
|
Slot Format Indication on the given cell
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
SP-CSI-RNTI
|
Activation of Semi-persistent CSI reporting on PUSCH
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
CI-RNTI
|
Cancellation indication in UL
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
PS-RNTI
|
DCP to indicate whether to start drx-onDurationTimer for associated DRX cycle
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
SL-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled sidelink transmission
|
SL-SCH
|
SCCH, STCH
|
|
SLCS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled sidelink transmission (activation, reactivation and retransmission)
|
SL-SCH
|
SCCH, STCH
|
|
SLCS-RNTI
|
Configured scheduled sidelink transmission (deactivation)
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
SL Semi-Persistent RNTI
|
Semi-Persistently scheduled sidelink transmission
|
SL-SCH
|
STCH
|
|
SL Semi-Persistent Scheduling V2X-RNTI
|
Semi-persistent V2X scheduled transmission
|
SL-SCH
|
N/A
|
|
SL Semi-Persistent Scheduling V2X-RNTI
|
Semi-persistent V2X scheduled transmission (activation, reactivation and retransmission)
|
SL-SCH
|
N/A
|
|
SL Semi-Persistent Scheduling V2X-RNTI
|
Semi-persistent V2X scheduled transmission (deactivation)
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
G-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled MBS PTM
|
DL-SCH
|
MTCH
|
|
G-RNTI
|
Dynamically scheduled MCCH signaling and MCH change notification
|
DL-SCH
|
MCCH
|
|
PEI-RNTI
|
MCCH change indication
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
NOTE 1: The usage of MCS-C-RNTI is equivalent to that of C-RNTI in MAC procedures (except for the C-RNTI MAC CE).
NOTE 2: The MAC entity uses SL Semi-Persistent Scheduling V-RNTI to control semi-persistently scheduled sidelink transmission on SL-SCH for V2X sidelink communication as specified in clause 5.14.1.1 of TS 36.321
|
What kind of RNTI should be used ?
This is determined by the type of the DCI and Physical channel that a UE need to decode. These are well summarized by 3GPP specification as shown below.
< 38.202 v17.2 - Table 6.2-1: Downlink "Reception Types" >
|
Reception Type
|
Physical Channel
|
Monitored RNTI
|
Associated Transport Channel
|
Comment
|
|
A
|
PBCH
|
N/A
|
BCH
|
|
|
B
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
SI-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
Note 1
|
|
C0
|
PDCCH
|
P-RNTI
|
N/A
|
Note 1, Note 2
|
|
C1
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
P-RNTI
|
PCH
|
|
|
D0
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
RA-RNTI or Temporary C-RNTI or MsgB-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
Note 3
|
|
D1
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
C-RNTI, CS-RNTI, MCS-C-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
|
|
D2
|
PDCCH
|
C-RNTI, CS-RNTI, MCS-C-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
|
|
D3
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
G-RNTI, G-CS-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
Note 6
|
|
D4
|
PDCCH
|
G-CS-RNTI
|
N/A
|
Note 7
|
|
D5
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
MCCH-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
Note 8
|
|
D6
|
PDCCH+PDSCH
|
G-RNTI
|
DL-SCH
|
Note 9
|
|
E
|
PDCCH
|
C-RNTI
|
N/A
|
Note 4
|
|
F0
|
PDCCH
|
Temporary C-RNTI
|
UL-SCH
|
Note 3
|
|
F1
|
PDCCH
|
C-RNTI, CS-RNTI, MCS-C-RNTI
|
UL-SCH
|
|
|
G
|
PDCCH
|
SFI-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
H
|
PDCCH
|
INT-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
J0
|
PDCCH
|
TPC-PUSCH-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
J1
|
PDCCH
|
TPC-PUCCH-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
J2
|
PDCCH
|
TPC-SRS-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
K
|
PDCCH
|
SP-CSI-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
L0
|
PDCCH
|
SL-RNTI
|
SL-SCH
|
|
|
L1
|
PDCCH
|
SL-CS-RNTI
|
SL-SCH
|
|
|
M
|
PDCCH
|
SL Semi-Persistent Scheduling V-RNTI
|
SL-SCH
|
Note 5
|
|
N
|
PDCCH
|
PS-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
O
|
PDCCH
|
AI-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
P
|
PDCCH
|
CI-RNTI
|
N/A
|
|
|
Q
|
PDCCH
|
PEI-RNTI
|
N/A
|
Note 1
|
|
Note 1: These are received from PCell only.
Note 2: In some cases UE is only required to monitor the short message within the DCI for P-RNTI.
Note 3: These are received from PCell or PSCell.
Note 4: This corresponds to PDCCH-ordered PRACH.
Note 5: This corresponds to PDCCH scheduling LTE PC5.
Note 6: This is for multicast in RRC connected state.
Note 7: This corresponds to DL Semi-Persistent Scheduling release for multicast in RRC connected state.
Note 8: This is for broadcast MCCH.
Note 9: This is for broadcast MTCH. UE is not required to decode more than one PDSCH for MTCH simultaneously.
|
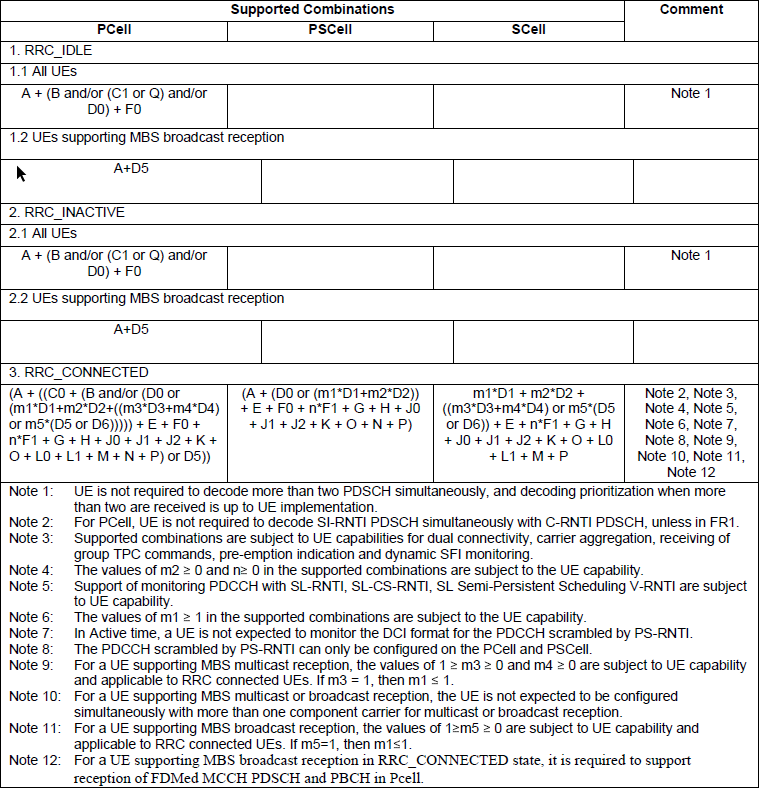
Should a UE has to try all different types of RNTI listed in the table above all the time to decode necessary DCIs ? It would be OK for UE to try all the RNTI, but it would be too much overhead and energy consuming. Usually there are only a few RNTI candiates for a specific call status. What kind of candidate RNTI is likely to be used for specific RRC States are summarized in 3GPP specification as shown below.
NOTE : Since the decoding of DCI is related to various search space, the note on SearchSpace would give you further insight
< 38.202 v17.2 - Table 6.2-2: Downlink Reception Type Combinations >
Reference
[1]
|
|

