|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
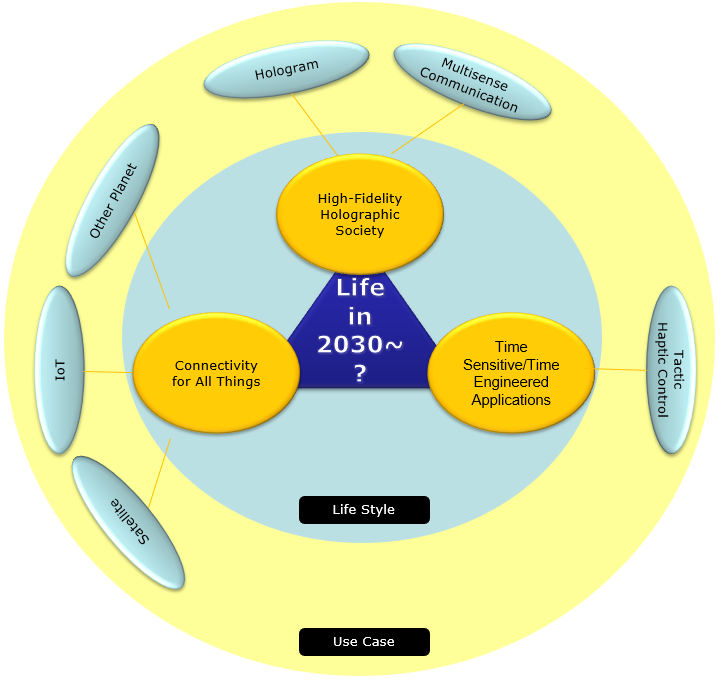
Simple answer is 'We don't know yet' -:). At least, as of Jul 2019 when I was writing the first note on this topic. But from various presentations and documents that I've gone through, it seems that we may identify a few pillars as we did at the early stages of 5G as shown below. I tried to set the three pillars as in 5G. It seems that the first two pillars Terahertz and AI/ML seems to the ones that are most commonly mentioned in the early discussion but I am not sure whether the third pillar High Data Rate in eMTC/URLLC can be a clear target for 6G or not.
Followings are the 6G overview from some important organizations and sources. ITUITU propose/outlines the capabilities and usage scenarios of IMT-2030 represent a comprehensive blueprint for the next generation of wireless communication technologies. The proposal outlines the strategic expansion from the existing 5G standards (IMT-2020) to the advanced features envisioned for 6G. They depict an ambitious set of enhancements and new capabilities aimed at transforming global connectivity, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as AI and advanced sensing, and significantly improving network performance across various metrics such as reliability, latency, and data rates. Together, these diagrams underscore a future where digital communication is more immersive, ubiquitous, and efficient, driven by overarching principles of sustainability, security, and inclusivity in connecting the unconnected. 6G Use Case ScenarioThis diagram illustrates the six usage scenarios anticipated for the IMT-2030 (commonly referred to as 6G), which aims to extend and enhance the capabilities established by IMT-2020 (5G). This vision for 6G represents a significant leap forward in connectivity and communication. It promises not only to enhance existing applications but also to unlock entirely new possibilities in areas like immersive experiences, IoT, and AI.
Source : ITU's IMT2030 Usage scenarios Extension from IMT-2020 (5G)The Extension from IMT-2020 (5G) to IMT-2030 (6G) represents an ambitious leap in telecommunications technologies, seeking to build upon and expand the capabilities established by 5G networks. This progression aims to transform the landscape of digital communication by enhancing current services like Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and introducing next-generation capabilities such as immersive communication. It also seeks to elevate machine type communications and ultra-reliable low-latency operations to meet the burgeoning demands of various emerging technologies and applications.
New Scenarios Introduced in IMT-2030IMT-2030 introduces new scenarios that are set to redefine connectivity and technological integration. These include Ubiquitous Connectivity, which aims to provide comprehensive and high-quality network coverage to all areas, and AI and Communication, which seeks to integrate artificial intelligence deeply within network infrastructures to optimize and personalize user experiences. Additionally, the Integrated Sensing and Communication scenario plans to harness the network for environmental sensing, thereby creating smarter and more responsive technology ecosystems.
Overarching AspectsThe Overarching Aspects of IMT-2030 encapsulate the core principles that will guide the development and deployment of 6G technologies. These principles include Sustainability, emphasizing the importance of eco-friendly approaches; Connecting the Unconnected, which aims to expand digital access to underserved areas;
6G CapabilitiesFollowing diagram outlines the envisioned capabilities for IMT-2030, which is often associated with the future 6G technologies. It categorizes these capabilities into existing enhancements over 5G (shown in green) and entirely new capabilities unique to 6G (shown in blue). This diagram illustrates that the range of values provided for each capability are targets for future research and have equal priority. This means that for any given usage scenario, multiple or single values might be explored and further developed into specific recommendations or standards in future ITU-R publications. This strategic approach ensures a comprehensive development towards realizing the ambitious goals set for the next generation of telecommunications technologies.
Source : Capabilities of IMT 2030 Enhanced Capabilities from IMT-2020 (5G)
New Capabilities Unique to IMT-2030
NEXTG AllianceNEXTG Alliance outlines two topics "6G Usage Scenarios and Capabilities" and "6G Requirements & Design Considerations" and the two topics collectively provide a detailed overview of the strategic foundation and operational blueprint for the development of the sixth generation of mobile communications technology, 6G. "6G Usage Scenarios and Capabilities" outlines the broad usage scenarios and new capabilities that 6G aims to support, illustrating a forward-thinking approach to immersive, massive, and ultra-reliable communication technologies. It emphasizes the enhancements over current 5G technologies and introduces new dimensions such as AI integration and improved environmental sensing capabilities. "6G Requirements & Design Considerations" delves deeper into the specific requirements and design considerations necessary to implement these advanced 6G capabilities. It segments the core prerequisites into Essential Needs, Use Case Requirements, and Design Considerations, each category meticulously detailing what will be required to effectively develop and deploy a robust 6G network. This includes everything from ensuring digital inclusion and energy efficiency to addressing complex design challenges related to system architecture and reliability. Together, these tables present a comprehensive vision for 6G, highlighting both the ambitious goals and the practical steps needed to achieve them, thus setting the stage for a transformative impact on global connectivity and technological innovation. 6G Position Statement : An Operator ViewFollowing table provides a structured overview of the strategic framework guiding the development of IMT-2030, the next evolution in telecommunications technology envisioned to succeed 5G. It outlines four key areas: Innovations & Services, Operational Priorities, Guiding Principles, and Spectrum considerations. Each category encapsulates essential objectives and strategies, from enhancing interoperability and integrating advanced network features to emphasizing sustainability through energy reduction and security by design. Additionally, it addresses the importance of global standards and the need for a robust spectrum strategy to accommodate evolving technological demands. This holistic approach ensures that future telecommunications infrastructure will not only support increased connectivity demands but also advance in a manner that is sustainable, secure, and adaptable to future innovations.
6G Requirements & Design ConsiderationsNEXTG Alliance delineates a comprehensive framework essential for shaping the future of telecommunications with the advent of 6G technology. It categorizes the core elements into three main sections: Essential Needs, Use Case Requirements, and Design Considerations. These components collectively outline the critical areas of focus that will drive the development and implementation of 6G networks. The "Essential Needs" segment underscores the fundamental requirements such as digital inclusion and energy efficiency, vital for creating an inclusive and sustainable technological ecosystem. "Use Case Requirements" detail specific operational needs including mobility, connectivity, and AI integration that 6G must address to support advanced applications and services. Lastly, "Design Considerations" focus on the architectural and functional attributes necessary to ensure that the network is capable of meeting the defined requirements with optimal performance, security, and flexibility. This structured approach emphasizes the multifaceted planning required to realize the potential of 6G in meeting future digital demands comprehensively.
Snapshots from other sourcesHere I am compiling snapshots from various other sources including mine. Just take a quick look at the diagram and you can easily make your own stories.
Following illustrations shows a 6G definition by Huawei. As you see, eMBB, mMTC, URLLC would take evolutionary path into 6G and Network Sensing will become a new pillar in 6G. All the components will be coordinated / controlled by AI in 6G.
Source : 6G: The Next Horizon
Source : Drawn based on 6G Wireless Systems: Vision,Requirements, Challenges,Insights, and Opportunities
YouTube
YouTube (Korean)
NOTE : If you are not a korean speaker, you may use AI (e.g, chatGPT plugins) to get the english summary of these video. 3GPP
Readings
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



 Source :
Source :  Source :
Source :