|
C/C++ |
||
|
Explanation will be posted later !
Example 1 > ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
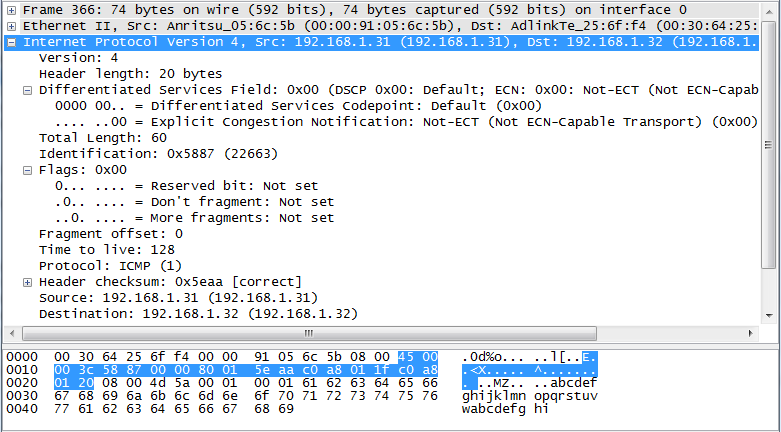
In this example, I will show you an example showing the IPv4 header as shown below.
Following is the source code that I will compile with Microsoft .Net 2008 VC++.
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <tchar.h>
// Followings are data type casting that will be used for converting Endianess (Convering Big // Endian to little Endian and Little Endian to Big Endian) typedef signed short int int16_t; typedef unsigned short int uint16_t; typedef signed int int32_t; typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
// Following data structure for IPv4. // NOTE : According to IPv4 header structure, I should define 'unsigned char ip_Version:4 // ,ip_HeaderLength:4 ' instead of 'unsigned char ip_HeaderLength:4, ip_Version:4'. This is because // Windows is using the Little Endian. You should change the order of these two fields based on // the system you are running the code.
typedef struct header { unsigned char ip_HeaderLength:4, ip_Version:4; unsigned char ip_ServiceType; unsigned short int ip_TotalLength:16; unsigned short int ip_Identification:16; unsigned short int ip_FragmentOffset:16; unsigned char ip_TimeToLive:8; unsigned char ip_Protocol:8; unsigned short int ip_Checksum:16; unsigned char ip_Source[4]; unsigned char ip_Destination[4];
} ipv4Header;
// Following APIs are to swap the Endianness (Type of Endian). Little to Big, Big to Little uint16_t swap_uint16( uint16_t val ) { return (val << 8) | (val >> 8 ); }
int16_t swap_int16( int16_t val ) { return (val << 8) | ((val >> 8) & 0xFF); }
uint32_t swap_uint32( uint32_t val ) { val = ((val << 8) & 0xFF00FF00 ) | ((val >> 8) & 0xFF00FF ); return (val << 16) | (val >> 16); }
int32_t swap_int32( int32_t val ) { val = ((val << 8) & 0xFF00FF00) | ((val >> 8) & 0xFF00FF ); return (val << 16) | ((val >> 16) & 0xFFFF); }
// Following is the main part of this example int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) {
ipv4Header hIPv4;
// Following is Byte Array that will be used in this example. This example is from // the wireshark log shown above. In real application, you may get this data from // other source like binary file or network interface card.
unsigned char ipPacket[] = { 0x45, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3C, 0x58, 0x87, 0x00, 0x00, 0x80, 0x01, 0x5E, 0xAA, 0xC0, 0xA8, 0x01, 0x1F, 0xC0, 0xA8, 0x01, 0x20, 0x08, 0x00, 0x4D, 0x5A, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x01, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66, 0x67, 0x68, 0x69, 0x6A, 0x6B, 0x6C, 0x6D, 0x6E, 0x6F, 0x70, 0x71, 0x72, 0x73, 0x74, 0x75, 0x76, 0x77, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66, 0x67, 0x68, 0x69 };
// Copy the block of data from ipPacket and assign them to hIPv4 // By this line, the data is automatically split into each items defined in ipv4Header memcpy(&hIPv4,ipPacket,sizeof(ipv4Header));
// Following is to print out the items analyzed by ipv4Header data structure. // You would see some value goes through Endian Swap function before it get printed out. // If you are using this example on Big Endian system, you would not need to use these // Endian Swap function. printf("Version :%d\n",hIPv4.ip_Version); printf("Header length :%d Bytes\n",hIPv4.ip_HeaderLength*4); printf("Service :%#02x\n",hIPv4.ip_ServiceType); printf("Total Length :%d\n",swap_uint16(hIPv4.ip_TotalLength)); printf("Identification :%#x (%d)\n",swap_uint16(hIPv4.ip_Identification) ,swap_uint16(hIPv4.ip_Identification)); printf("Fragment Offset :%d\n",swap_uint16(hIPv4.ip_FragmentOffset)); printf("Time To Live :%d\n",hIPv4.ip_TimeToLive); printf("Protocol :%d\n",hIPv4.ip_Protocol); printf("Checksum :%#x\n",swap_uint16(hIPv4.ip_Checksum)); printf("Source : %d.%d.%d.%d\n",hIPv4.ip_Source[0] ,hIPv4.ip_Source[1] ,hIPv4.ip_Source[2] ,hIPv4.ip_Source[3]); printf("Destination : %d.%d.%d.%d\n",hIPv4.ip_Destination[0] ,hIPv4.ip_Destination[1] ,hIPv4.ip_Destination[2] ,hIPv4.ip_Destination[3]);
return 0; }
Result >
Version :4 Header length :20 Bytes Service :00 Total Length :60 Identification :0x5887 (22663) Fragment Offset :0 Time To Live :128 Protocol :1 Checksum :0x5eaa Source : 192.168.1.31 Destination : 192.168.1.32
|
||