|
Bluetooth Specification
Bluetooth technology has become ubiquitous in the modern world, embedded in everything from smartphones to kitchen appliances. Understanding its specifications, including the different classes, ranges, and profiles, is essential for appreciating its capabilities and limitations.

Bluetooth specification is defined roughly by two large criteria : Range and Profile. Range is about the coverage (maximum distance between the devices) and Profile is about the feature/functionaility the device supports.
Classe and Range defines how far a bluetooth device can pair and communicate with other devices. Each class of Bluetooth has its own range and power, orchestrating a world of devices in seamless connectivity.
From the robust Class 1, broadcasting its signal up to 100 meters, to the subtle whisper of Class 3, designed for intimate ranges – understanding these classes is key to mastering the art of wireless communication. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of Bluetooth classes and their ranges, and discover how they shape the wireless world around us."
Bluetooth devices are classified into three main classes based on their power and range capabilities:
- Class 1: These are the most powerful, designed for long-range communication, with a maximum power output of 100mW (20 dBm). They can achieve ranges of up to 100 meters or 328 feet in optimal conditions. Class 1 devices are typically used in industrial tools where long-range communication is necessary.
- Class 2: The most common class found in mobile devices, Class 2 Bluetooth devices have a power output of 2.5mW (4 dBm) and a standard range of approximately 10 meters or 33 feet. This class is suitable for short-range applications such as wireless keyboards, mice, and headsets.
- Class 3: The least powerful, with a maximum power output of 1mW (0 dBm), these devices are limited to short-range communication of about 1 meter or 3 feet. They are less common and are often used for devices that require minimal power consumption and data transfer over short distances.
Imagine Bluetooth profiles as special languages that electronic devices use to talk to each other. Just like people need to speak the same language to understand one another, devices use these profiles to connect and share information easily. Whether it’s listening to songs, making calls without using your hands, or checking how many steps you’ve walked, profiles are the secret to making different gadgets work together smoothly. They are the invisible helpers that make using all our wireless
gadgets a simple and enjoyable experience.
To ensure interoperability among devices, Bluetooth uses standardized profiles—specifications for how different types of data are communicated.
Some of the most common profiles include:
- Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP): This profile defines how high-quality audio can be streamed from one device to another over a Bluetooth connection. It’s the standard for wireless audio streaming, used in wireless speakers and headphones.
- Examples
- Wireless headphones and earbuds
- Bluetooth-enabled car audio systems
- Portable Bluetooth speakers
- Smart TVs with Bluetooth audio support
- Object Push Profile (OPP): OPP is used for sending objects such as pictures, virtual business cards, or appointment details. It’s typically used for the transfer of files and media between devices without requiring a complex setup or high bandwidth.
- Examples
- Smartphones for transferring contacts and files
- Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs)
- Computers with Bluetooth transfer capabilities
- Hands-Free Profile (HFP): This profile allows users to make and receive calls via Bluetooth. It’s widely used in car systems and headsets to enable hands-free calling, essential for safe driving.
- Examples
- Bluetooth car kits
- Wireless headsets for hands-free calling
- Smartwatches with call answering features
- Headset Profile (HSP): Similar to HFP, the HSP provides the basic functionalities required for communication between a mobile phone and a headset. It supports the audio transmission to and from the headset.
- Example
- Bluetooth-enabled telephone headsets
- Gaming headsets with Bluetooth connectivity
- Virtual reality headsets with Bluetooth functions
- File Transfer Profile (FTP): FTP is used for browsing, manipulating, and transferring files between devices. This profile facilitates the management of file directories and file manipulation operations like copying and deleting.
- Examples
- Smartphones and tablets for file management
- Laptops and desktop computers with Bluetooth
- Digital cameras with Bluetooth file transfer feature
- Personal Area Networking Profile (PAN): This profile is used to create an internet connection between devices or connect several devices to communicate with each other without internet access.
- Examples
- Computers and laptops for creating a network
- Smartphones for internet sharing via Bluetooth tethering
- Printers that connect to a Bluetooth network
- Audio/Video Remote Control Profile (AVRCP): This profile allows for remote control of media playback on other devices. It supports actions like play, pause, skip, and volume control. It's commonly used in car stereo systems to control music from your phone or in wireless headphones with buttons to control your music without taking your phone out.
- Examples
- Wireless stereo controls
- Media playback remotes
- Smart speakers with remote control capabilities
- Human Interface Device (HID): HID is used for wireless keyboards, mice, joysticks, or other input devices to interact with computers, smartphones, or gaming consoles. It helps in transferring input data over Bluetooth, allowing you to type, select, or play games wirelessly.
- Examples
- Bluetooth keyboards
- Wireless computer mice
- Game controllers with Bluetooth technology
- HID Over GATT Profile (HOGP): The HID Over GATT Profile, commonly abbreviated as HOGP, is a Bluetooth profile that enables wireless communication between devices using the Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) protocol. It allows low-power devices like peripherals to interface with other devices over Bluetooth, providing input and control functionalities. This profile is built on top of the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) and is tailored for devices that need to operate with minimal energy consumption, extending battery life while maintaining a wireless connection.
- Examples
- Wireless Keyboards
- Bluetooth Mice:
- Gaming Controllers
- Fitness Trackers
- Smart Pens
- Health Device Profile (HDP): HDP is designed for health-related devices to send data to monitoring equipment, like a blood pressure monitor sending readings to your doctor's computer. It's vital for telehealth services, where patient data needs to be shared securely and reliably over a distance.
- Examples
- Wireless heart rate monitors
- Bluetooth-enabled blood pressure cuffs
- Fitness trackers that sync health data to other devices
- Basic Imaging Profile (BIP): BIP allows for the wireless transfer of images between devices, enabling functions like sending photographs from a digital camera to a printer or computer without needing a physical connection. It's also used in smartphones for sharing images with other Bluetooth-enabled devices, simplifying the process of managing and distributing digital photos.
- Examples
- Digital cameras that send images to printers or computers
- Smartphones for image sharing with other devices
- Medical imaging devices with Bluetooth capability
- Video Distribution Profile (VDP) : VDP is designed to allow the transmission of video content between devices over a Bluetooth connection. It's used for streaming video content from a source device, like a smartphone or tablet, to a receiving device, such as a television or monitor equipped with Bluetooth capabilities. However, due to bandwidth limitations of Bluetooth compared to other technologies like Wi-Fi, VDP is less common for high-definition video streaming
Once you got overall understandings explained above, you would make sense out of bluetooth datasheet for various products. Let me share some example datasheets here.
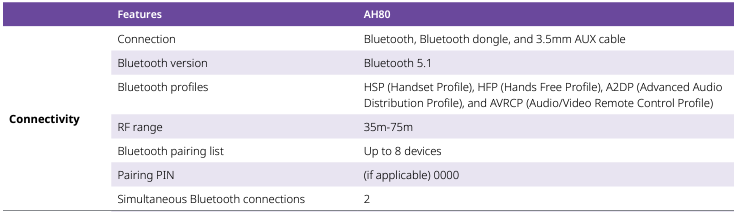
Source : Alcatel-Lucent Enterprise AH80 Bluetooth Headset
This is a little bit detailed description of each items in the datasheet.
- Connection:
- The device can connect via Bluetooth, a Bluetooth dongle, and a 3.5mm AUX cable. This implies it offers both wireless and wired connection options.
- Bluetooth version:
- It supports Bluetooth version 5.1, which offers improvements over its predecessors in terms of range, connection speed, and overall communication efficiency.
- Bluetooth profiles:
- The listed profiles indicate the device’s capabilities: Refere to profile section explained above.
- RF range:
- The radio frequency range is 35m-75m, which is the distance over which the device can maintain a stable Bluetooth connection with another device. This is a relatively broad range and suggests it may operate efficiently at varying distances, possibly using Bluetooth 5.1's improved range capabilities.
- Bluetooth pairing list:
- The device can remember up to 8 different Bluetooth connections, making it easier to switch between multiple source devices without needing to re-pair each time.
- Pairing PIN:
- If applicable, the default PIN for pairing is "0000", a common default for Bluetooth devices.
- Simultaneous Bluetooth connections:
- It can maintain two Bluetooth connections at the same time. This is useful for switching between two source devices, such as a phone and a tablet, without disconnecting one to use the other.

Source : Microsoft Bluetooth Mouse
This is detailed description about the datasheet.
- Wireless platform:
- The device uses Bluetooth version 5.0 Low Energy (LE), which is optimized for devices that require low power consumption while maintaining communication capability. Bluetooth LE is ideal for IoT devices, wearables, and sensors because it allows for long battery life.
- Wireless Frequency:
- The product operates in the 2.4GHz frequency range, which is the standard frequency for Bluetooth and many other wireless communications technologies. This frequency allows for worldwide use without the need for different models for different regions.
- Wireless Range:
- The device has a wireless range of 33 feet (10 meters) in open air, which is typical for many Bluetooth devices. However, in a typical office environment, which likely has walls and other obstructions, the range is reduced to 16 feet (5 meters). This indicates that the device's signal can be impeded by physical barriers, which is common for Bluetooth devices.
- Bluetooth Profile Support:
- It supports the HID Over GATT Profile (HOGP). This profile is used to connect Human Interface Devices (like keyboards, mice, or game controllers) over Bluetooth using the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT). It's specifically designed for Bluetooth Low Energy devices, enabling efficient data exchange for user inputs.
|
|


