|
C/C++ |
||
|
Graph Construction
This is sample code that is to implement the graph explained in Algorithm : Graph Construction. Refer to the page to understand the concept,
#include <malloc.h> #include <stdio.h>
// A structure to represent a node in the adjacency list. typedef struct NODE { int data; struct NODE *next; } node;
// A structure to represent list of vertexes(Node) typedef struct VERTEXLIST { node *vlisthead; } vertexlist;
// A structure to store the graph vertexes. This will store an Array // and each element of the array will point to the head of a linked list typedef struct GRAPH { int v; vertexlist *vl; } Graph;
// A function to declare the graph. This will create an array that will store the head of each // linked list. Each of the linked list will store the nodes that are connected to a specific node Graph* CreateGraph(int n) { int i;
Graph *vlist; vlist = (Graph*) malloc(sizeof(Graph));
// store the number of nodes given by the user vlist->v = n;
// allocate a block of memory location for the array that will store the head // for each of the linked list vlist->vl = (vertexlist*) malloc(sizeof(vertexlist)*(n+1));
// Initialize the head to NULL. for(i = 0; i < n+1; i++) { vlist->vl[i].vlisthead = NULL; }
return vlist; }
// A function to add the edge into the graph. // This will add the node at the beginning of the linked list for the node v1. void AddNode(Graph *G, int v1, int v2) {
node *newnode1; node *newnode2; node *temp;
newnode1 = (node*) malloc(sizeof(node)); newnode1->data = v1; newnode1->next = NULL;
newnode2 = (node*) malloc(sizeof(node)); newnode2->data = v2; newnode2->next = NULL;
// Connection v1 to v2. if(G->vl[v1].vlisthead == NULL) { // If the head is null, insert the newnode2(v2) to the head of the linked list // that stores all the nodes that are connected to the node v1. G->vl[v1].vlisthead = newnode2; } else { // Otherwise, add the node at the beginning of the linkedlist. newnode2->next = G->vl[v1].vlisthead; G->vl[v1].vlisthead = newnode2; } }
int main() { int i, v = 4;
Graph *G = CreateGraph(v);
AddNode(G, 1, 3); AddNode(G, 3, 2); AddNode(G, 4, 1); AddNode(G, 4, 3);
printf("\n\nLinkedList representaion of the Incidence Matrix for a graph: "); for(i = 0; i < v; i++) { printf("\n\tV(%d) -> {",i+1); while(G->vl[i+1].vlisthead != NULL) { printf(" %d",G->vl[i+1].vlisthead->data); G->vl[i+1].vlisthead = G->vl[i+1].vlisthead->next; } printf(" }"); } }
Result :------------------------------------------------------
LinkedList representaion of the Incidence Matrix for a graph: V(1) -> { 3 } V(2) -> { } V(3) -> { 2 } V(4) -> { 3 1 }
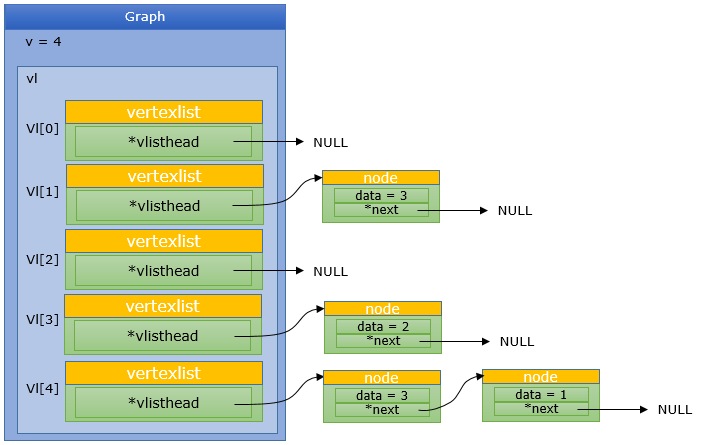
Now let me visualize what each of the code does.
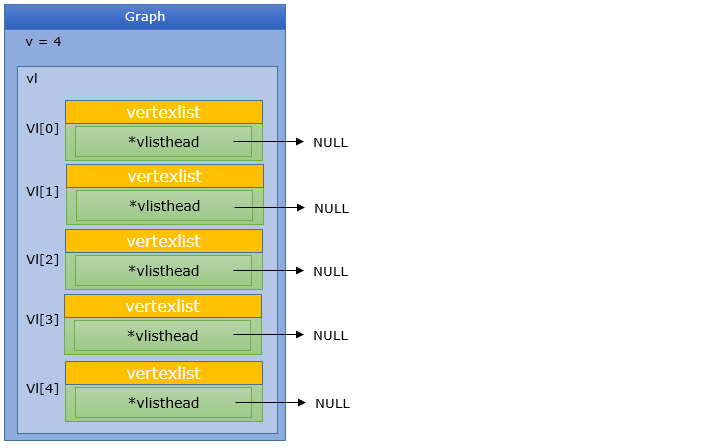
Graph *G = CreateGraph(v);
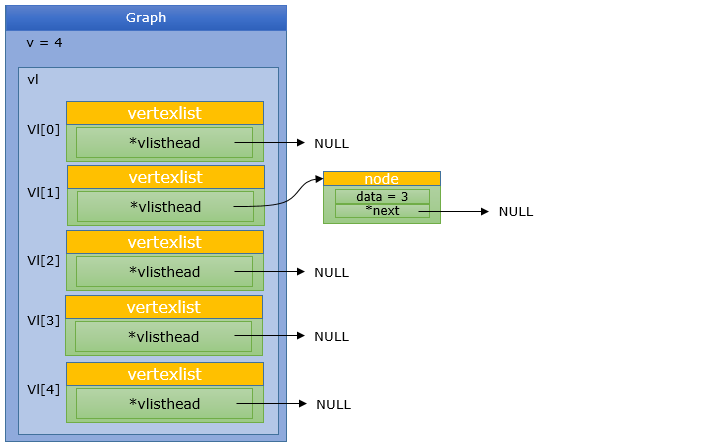
AddNode(G, 1, 3);
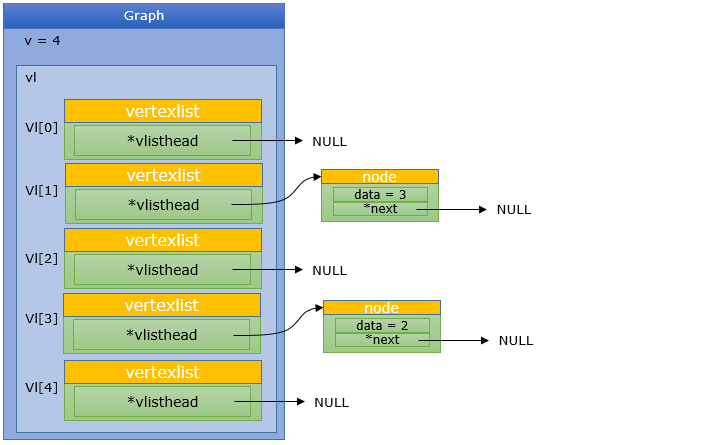
AddNode(G, 3, 2);
AddNode(G, 4, 1);
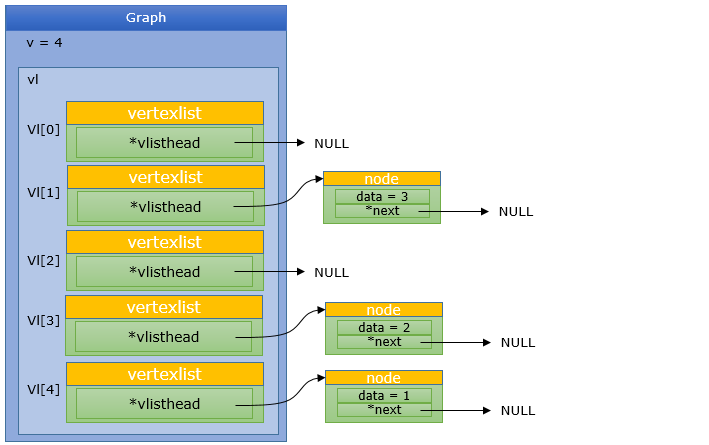
AddNode(G, 4, 3);
|
||