|
SIP Header : Via
Via header is a kind of queue that records all the message delivery path from the sender to final reciever. Once a message have all of the path in Via header, the reponse message only have to follow the addresses in Via header in reverse order and it will reach the initiator of the message. I think following illustration would better explain than my writing. As you see,
the main purpose of Via header is to provide the responder with the exact delivery path information so that the response message can successfully delivered to the initiator.
In short, the Via header in SIP is essential for routing SIP requests through the network and ensuring the proper delivery of responses. It records the path that the request has taken through various SIP proxies or servers to reach the final recipient. The Via headers create a record of the route taken by a SIP request, which is crucial for ensuring that the responses can be correctly routed back to the originator, following the exact reverse path through the SIP network.
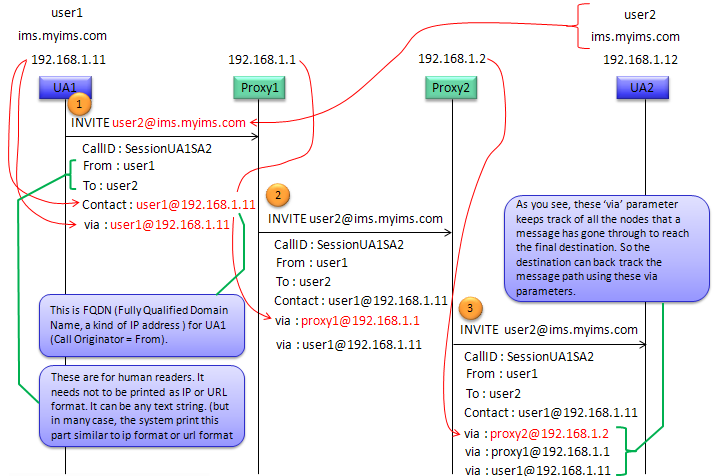
Followings are a few more highlights based on the diagram.
- Tracking the Route: Each proxy that the request passes through adds its own Via header to the request. This way, a SIP response can follow the reverse path back to the originator. It ensures that the response takes the same route back through the network as the original request.
- Route Information: The Via header includes the transport protocol, the proxy's IP address or hostname, and potentially a port number. It also contains a branch parameter, which helps in identifying and managing transactions.
- INVITE Request: In the scenario depicted, User Agent 1 (UA1) sends an INVITE request to User Agent 2 (UA2) to initiate a call. The INVITE passes through two proxies (Proxy1 and Proxy2).
- At UA1: The INVITE starts with UA1's Via header, containing UA1's information.
- At Proxy1: Proxy1 adds its Via header and forwards the INVITE to Proxy2.
- At Proxy2: Proxy2 adds its Via header and forwards the INVITE to UA2.
- Response Path: When UA2 sends a response, it will use the Via headers to determine the path back to UA1. The response will be sent to Proxy2, then to Proxy1, and finally back to UA1.
- Non-Human-Readable Identifiers: It's noted that the information in the Via headers is for routing purposes and doesn't need to be human-readable. It can appear in various formats, not limited to IP addresses or URLs.
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN): In the Contact header, the FQDN represents the address at which UA1 can receive responses directly. It's distinct from the Via header but is still used for routing SIP messages.
|
|
