|
Ethernet : 40 GbE/100 GbE(Gigabit Ethernet)
40 Gigabit Ethernet (40GbE) is a standard that enables the transfer of Ethernet frames at speeds of up to 40 gigabits per second (Gbps). It is intended mainly for local server connectivity (Note : 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) is intended for Internet backbones.)
40 GbE runs on Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable (QSFFP) cabling, a high-density fiber connector with 12 strands of fiber.
40GbE (100GbE as well) fulfill the following requirements and objectives:
- Support Full Duplex Ethernet MAC
-
Preserve existing 802.3 frame format, minimum size, and maximum size.
-
Preserve existing 802.3 MAC
-
Support high-bandwidth applications such as video on demand (VoD) and high-performance computing (HPC).
-
Support high-speed switching, routing, and application functions in data centers.
-
Exhibit a bit error rate (BER) of 10-12 or better
-
Support MAC data rate of 40 Gbs (40 GbE) - PHY requirement is as below
-
at least 10 km on Single Mode Fiber (SMF)
- at least 100 m on OM3 Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
- at least 150 m on OM4 Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
- at least 7 m on copper cable assembly
- at least 1 m on backplane
- Support MAC data rate of 100 Gbs (100 GbE) - PHY requirement is as below
- at least 10 km on Single Mode Fiber (SMF)
- at least 100 m on OM3 Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
- at least 150 m on OM4 Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
- at least 40 km on Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
- at least 7 m on copper cable assembly
-
Provide support for optical transport network (OTN).
-
Provide specifications for operation over single-mode optical fiber, laser optimized multimode optical fiber, copper cables, and backplanes.
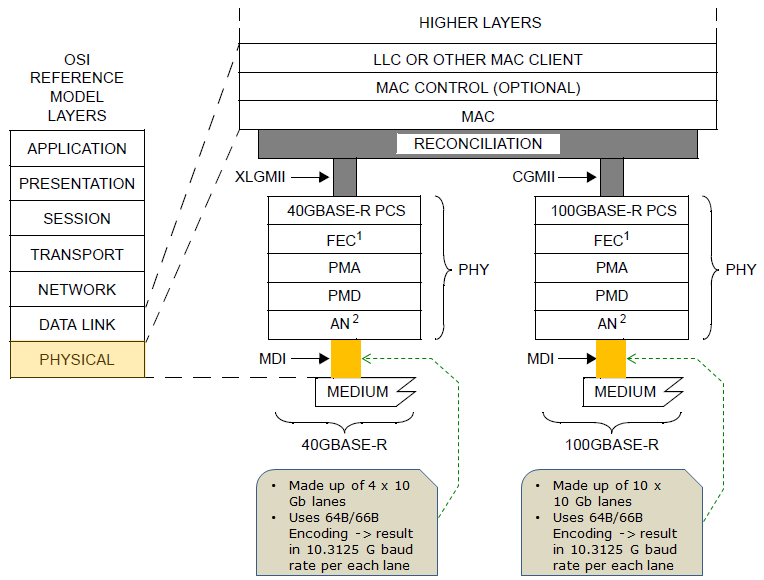
Overal Phyical layer for 40GbE and 100 GbE is structured as shown below in IEEE 802.3 Section 6. 40 GbE and 100 GbE is almost indential except the number of parallel lanes of MDI (Medium Dependent Interface).
|
|
