|
T3470
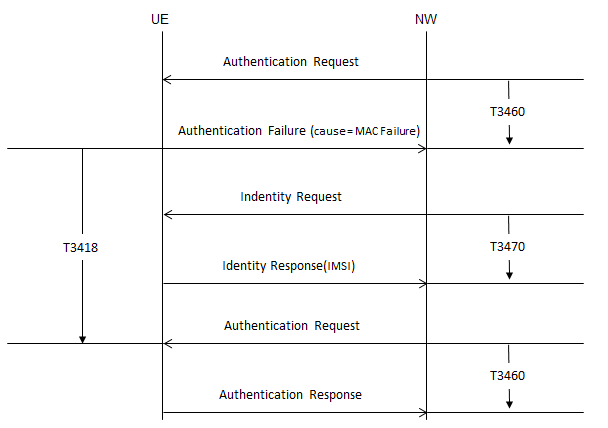
Purpose of T3470: Timer T3470 is used in the Identification Procedure to ensure that the network receives a timely response from the User Equipment (UE) after sending an IDENTITY REQUEST message. The timer supervises the communication and manages retransmissions or terminations if the procedure cannot be completed.
Timer T3470 plays a critical role in:
- Ensuring timely identification of the UE.
- Allowing recovery from temporary communication failures by managing retransmissions.
- Preventing indefinite delays in network procedures by terminating stalled identification processes.
- Managing procedural collisions, such as prioritizing attach requests over identification when applicable.
Key Scenarios Involving T3470
Identification Procedure:
- Initiation: When the network sends an IDENTITY REQUEST message to the UE, it starts timer T3470. This message specifies the type of identity being requested (e.g., IMSI, IMEI).
- Completion: Upon receiving the IDENTITY RESPONSE from the UE, the network stops T3470. The received identity information is then used to proceed with further signaling or authentication.
Abnormal Cases on the Network Side:
- Lower Layer Failures:
- If a lower layer failure is detected before the IDENTITY RESPONSE is received, the network stops T3470 and aborts the identification procedure as well as any ongoing EMM procedure.
- Timer T3470 Expiry:
- If T3470 expires before the IDENTITY RESPONSE is received:
- The network retransmits the IDENTITY REQUEST message and resets T3470.
- This process is repeated up to four times.
- On the fifth expiry:
- The network aborts the identification procedure.
- Any related ongoing EMM procedure is also terminated.
- Collision with an Attach Procedure:
- If the network receives an ATTACH REQUEST message while an identification procedure is ongoing, it checks whether there is a pending attach procedure:
- If no pending attach procedure exists (e.g., no ATTACH ACCEPT/REJECT message waiting to be sent), the network stops T3470 and proceeds with the new attach procedure.
|
|
