|
Mechanical Engineering |
||
|
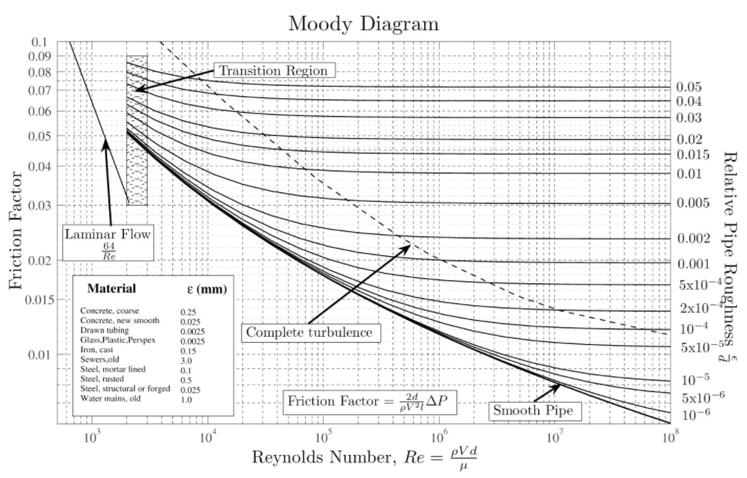
Fluid Mechanics : Moody's Diagram
Moody’s diagram is used to compute for the friction factor in the pipe that a working fluid flows across. Friction factor is dependent on the following:
The friction factor is a function of both Reynold’s Number of the working fluid and relative roughness of the pipe. The Moody diagram looks like this:
Tips for quick estimation on Friction Factor
Apply the following procedures to compute friction factor in a timely manner: i) Calculate the Reynold’s number(Re) of the flow to analyze the type of flow ii) If Re>2000, calculate the relative roughness of the pipe. If Re<2000, then friction factor is equal to 64/Re iii) Highlight the entire curve closest to the relative roughness of the pipe. iv) Using a ruler, extend a vertical line from Re to see where it intersects with the highlighted curve. Make a large mark on the intersection v) Using a ruler, extend a horizontal line to the left from the point of intersection from step iv)
|
||