|
3G/UMTS |
||
|
CN Domain Identity
Most of UMTS Cell support both CS and PS communication, but there are some cases where a cell support or allow only CS or PS communication. How Network can inform UE of its CN (Core Network) capability ? The first level information about CN capability is sent to UE by System Information Type 1. Would this capability influence on Registration protocol sequence ? Yes. There are roughly three different types of registration sequence being used for each of CN configuration. Of course, in real network you would see various variation.. but these three type of sequence would give you a good template for each case.
System Information Type 1
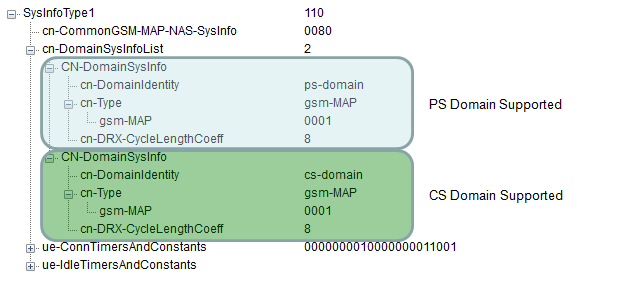
Following SIB1 shows the case where the cell support both CS and PS capability. In this case, usually Registration procedure < Type 1 > in case of Non Combined (NMO II) registration or < Type 3 > in case of Combined (NMO I) is used.
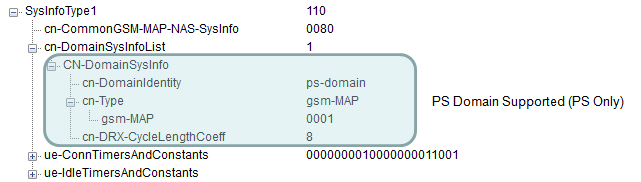
Following SIB1 shows the case where the cell support PS capability only. In this case, usually Registration procedure < Type 3 > is used.
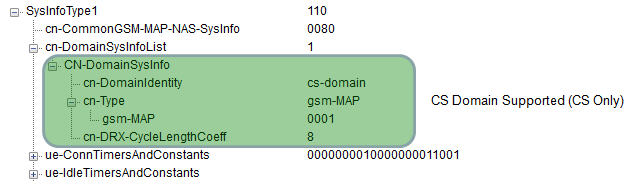
Following SIB1 shows the case where the cell support CS capability only. In this case, usually Registration procedure < Type 2 > is used.
Registration Sequence
< Type 1 > 1) RRC: RRC Connection Request 2) RRC: RRC Connection Setup 3) RRC: RRC Connection Setup Complete 4) RRC: initialDirectTransfer + MM: Location Updating Request 5) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + MM:Authentication Request 6) RRC: initialDirectTransfer + GMM: Attach Request 7) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + MM:Authentication Response 8) RRC : Security Mode Command 9) RRC : Security Mode Complete 10) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + MM:Identity Request 11) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + MM:Identity Response 12) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + MM:Location Updating Accept 13) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + MM:TMSI Reallocation Complete 14) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + GMM: AuthenticationAndCipheringRequest 15) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + GMM: AuthenticationAndCipheringResponse 16) RRC : Security Mode Command 17) RRC : Security Mode Complete 18) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Identity Request 19) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Identity Response 20) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Attach Accept 21) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Attach Complete 22) RRC : RRC Connection Release 23) RRC : RRC Connection Release Complete
< Type 2 > 1) RRC: RRC Connection Request 2) RRC: RRC Connection Setup 3) RRC: RRC Connection Setup Complete 4) RRC: initialDirectTransfer + MM: Location Updating Request 5) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + MM:Authentication Request 6) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + MM:Authentication Response 7) RRC : Security Mode Command 8) RRC : Security Mode Complete 9) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + MM:Identity Request 10) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + MM:Identity Response 11) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + MM:Location Updating Accept 12) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + MM:TMSI Reallocation Complete 13) RRC : RRC Connection Release 14) RRC : RRC Connection Release Complete
< Type 3 > 1) RRC: RRC Connection Request 2) RRC: RRC Connection Setup 3) RRC: RRC Connection Setup Complete 4) RRC: initialDirectTransfer + GMM: Attach Request 5) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + GMM: AuthenticationAndCipheringRequest 6) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + GMM: AuthenticationAndCipheringResponse 7) RRC : Security Mode Command 8) RRC : Security Mode Complete 9) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Identity Request 10) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Identity Response 11) RRC : downlinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Attach Accept 12) RRC : uplinkDirectTransfer + GMM:Attach Complete 13) RRC : RRC Connection Release 14) RRC : RRC Connection Release Complete
|
||