|
IP/Network |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SDN - OpenFlow
OpenFlow is a technology designed in University / Universities in order to test new ideas on networking algorithms or architecture. Of course, they can test their ideas on a small test environment (e.g, a couple of connected PCs or a single PC with multiple NICs) or using several specifially designed Hardwares (switches and routers). But Scaling would be one of the most important factors in any new networking technologies. You can never guarantee that a new idea proved working well with a small network with a small traffic works the same way in a real life networking environment. Is there any way to let the researchers verify their idea in real networking environement with real traffic in a campus ? This was the main motivation that created OpenFlow. Now with introduction of SDN (Software Defined Networking) and its possible adoption in 5G networking, OpenFlow start getting strong attention and becomes one of the strongest candiate for the standard SDN component.
Due to the situations described above, the researchers want to have network components that can provide following features as described in [1].
Technical Background for OpenFlow Switch
Putting forward requirements are easy, but letting the industry to realize the requirement is not easy. Especially it would be extremely difficult for Academia to change the moviding directions of industry players with big name. As a reconciliation, researchers tried to come up with a solution based on following observation (This is directly quoted from Ref [1]. I am blindly quoting this from the reference to let you get the first-hand feeling from the researchers).
The basic idea is simple: we exploit the fact that most modern Ethernet switches and routers contain flow-tables (typically built from TCAMs) that run at line-rate to implement firewalls, NAT, QoS, and to collect statistics. While each vendor’s flow-table is different, we’ve identified an interesting common set of functions that run in many switches and routers. OpenFlow exploits this common set of functions. OpenFlow provides an open protocol to program the flow-table in different switches and routers. A network administrator can partition traffic into production and research flows. Researchers can control their own flows - by choosing the routes their packets follow and the processing they receive. In this way, researchers can try new routing protocols, security models, addressing schemes, and even alternatives to IP. On the same network, the production traffic is isolated and processed in the same way as today.
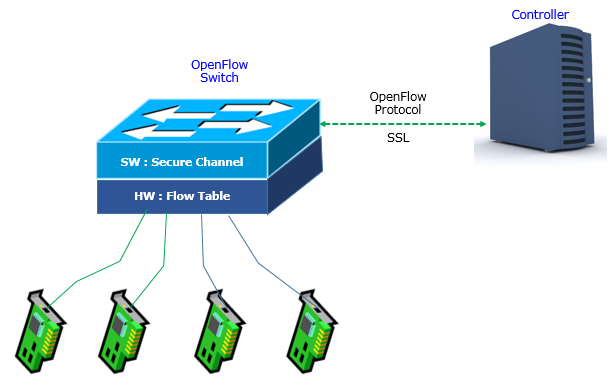
Overall structure of OpenFlow Switch described in the whitepaper ([1]) can be illustrated as shown below.
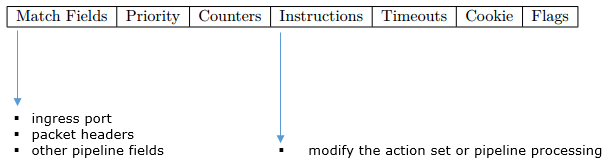
< OpenFlow Switch Specfication v1.5.0 - Table 1: Main components of a flow entry in a flow table >
There are three types of OpenFlow message types as listed below :
Controller-to-Switch message : As it implies, this is the type of message sent from Controller to Switch. The functionality of the messages is to manage or inspect the status of the switch.
Asynchronous message : This is the type of message sent from Switch to Controller. The functionality of the message is to update the Controller of network event and changes to the switch status.
Symmetric message : This is bidirectional message. It can be either from Switch to Controller or Controller to Switch.
Reference
[1] OpenFlow: Enabling Innovation in Campus Networks [2] OpenFlow Switch Specification - Version 1.5.0 ( Protocol version 0x06 ), December 19, 2014 [3] OpenFlow Switch Specification - Version 1.4.0 (Wire Protocol 0x05), October 14, 2013 [4] OpenFlow Switch Specification - Version 1.0.0 (Wire Protocol 0x01),December 31, 2009
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||