|
IoT(Internet Of Things) |
||
|
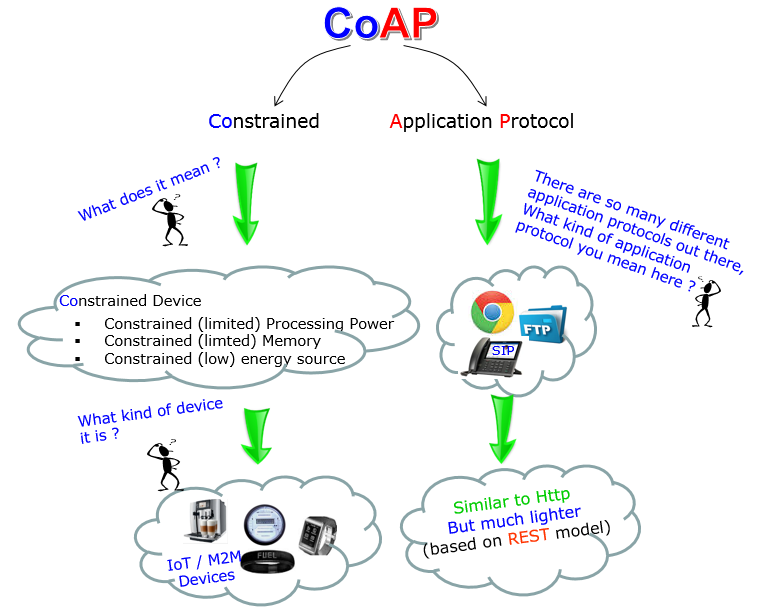
What is CoAP ?
CoAP stands for Constrained Application Protocol. The official definition of CoAP is defined in RFC 7252 as stated below.
The Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained (e.g., low-power, lossy) networks. The nodes often have 8-bit microcontrollers with small amounts of ROM and RAM, while constrained networks such as IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (6LoWPANs) often have high packet error rates and a typical throughput of 10s of kbit/s. The protocol is designed for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications such as smart energy and building automation. CoAP provides a request/response interaction model between application endpoints, supports built-in discovery of services and resources, and includes key concepts of the Web such as URIs and Internet media types. CoAP is designed to easily interface with HTTP for integration with the Web while meeting specialized requirements such as multicast support, very low overhead, and simplicity for constrained environments.
This definition can be illustrated as follows
Reference :
[1] How to learn CoAP in 5 minutes #IoTFriday (YouTube) [2] Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) Tutorial (YouTube), Slide for this presentation [3] Intro to REST (YouTube) [4] HTTP vs CoAP in one slide (Tweeter) [5] CoAP: The IETF's New Protocol for the Internet of Things (YouTube)
|
||