|
Plot3D
Like 2D plot, in 3D as well you would have most of functions that you can get from Matlab.
Draw a line between two points
This show how to draw a single line from (-1,-2,-3) to (1,2,3)
|
Filename : Line3D.py
|
|
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as axes3d
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
ax.plot([-1,1],[-2,2],[-3,3],'r--')
ax.set_xlim3d(-5, 5)
ax.set_ylim3d(-5, 5)
ax.set_zlim3d(-5, 5)
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
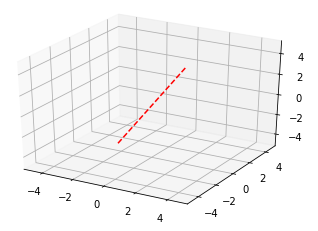
|
Drawing lines connecting multiple points
This show how to draw the line traces connecting multiple points
|
Filename : Line3D.py
|
|
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as axes3d
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
xList = [0,1,2,3,4]
yList = [-1,1,-1,1,-1]
zList = [2,-2,2,-2,2]
ax.plot(xList, yList, zList,'b')
ax.set_xlim3d(-5, 5)
ax.set_ylim3d(-5, 5)
ax.set_zlim3d(-5, 5)
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
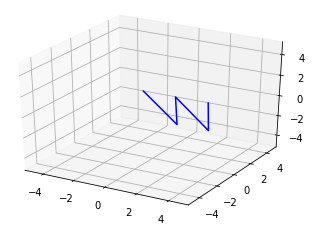
|
3D Parametric Plot
This show how to draw 3d Parameteric Plot
|
Filename : Line3D.py
|
|
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as axes3d
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
t = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, 100)
x = t
y = np.cos(t)
z = np.sin(t)
ax.plot(x, y, z,'b')
ax.set_xlim3d(0, t.max())
ax.set_ylim3d(-2, 2)
ax.set_zlim3d(-2, 2)
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
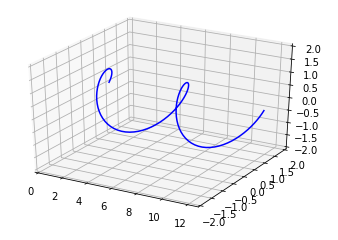
|
Surface Plot
This show how to draw 3d Parameteric Plot
|
Filename : plot3d_surce_01.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap='viridis')
# add labels and show the plot
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|

|
Contour Plot
This show how to draw 3d Contour Plot
|
Filename : plot3d_contour_01.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# plot filled contours
c = ax.contourf(X, Y, Z)
# add colorbar and labels
cb = fig.colorbar(c)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
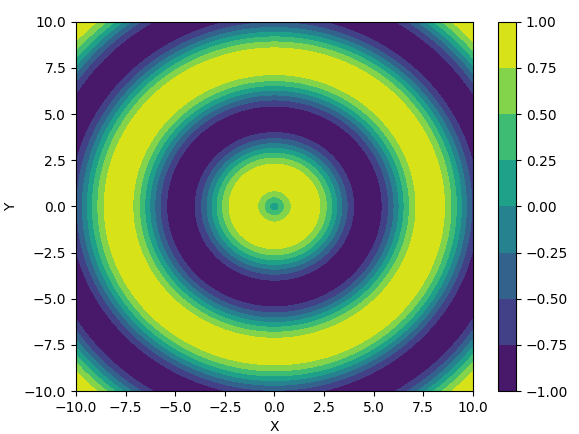
|
Removing Surface Color
This show how to remove the surface color. Use contour() function instead of contourf().
|
Filename : plot3d_contour_01.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# plot contours with single color or grayscale colormap
plt.contour(X, Y, Z, cmap='jet')
plt.colorbar()
# add labels
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|

|
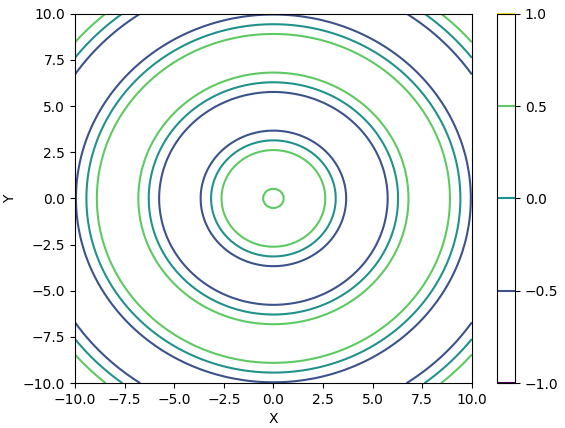
Changing Contour Level
|
Filename : plot3d_contour_01.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# plot contours with single color or grayscale colormap
levels = [-1.0, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1.0]
plt.contour(X, Y, Z, levels=levels)
plt.colorbar()
# add labels
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
|
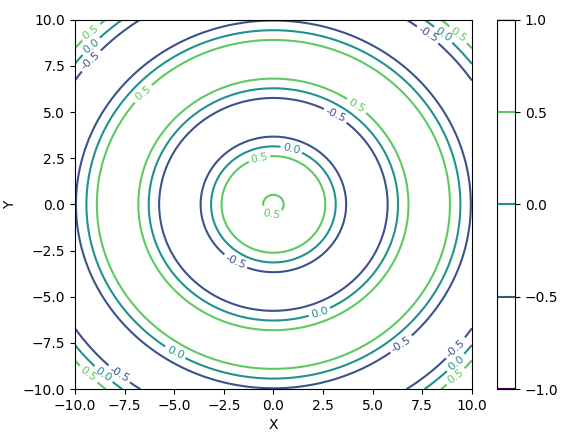
Printing Contour Level
|
Filename : plot3d_contour_01.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# plot contours with single color or grayscale colormap
levels = [-1.0, -0.5, 0, 0.5, 1.0]
contours = plt.contour(X, Y, Z, levels=levels)
plt.clabel(contours, inline=True, fontsize=8, fmt='%1.1f')
plt.colorbar()
# add labels
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
|
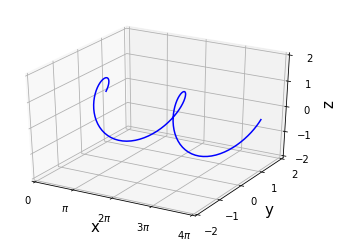
Ticks, Tick Mark, Axis Label
This show how to format tick mark,tick label,axis label
|
Filename : Line3D.py
|
|
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as axes3d
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
t = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, 100)
x = t
y = np.cos(t)
z = np.sin(t)
ax.plot(x, y, z,'b')
ax.set_xlim3d(0, t.max())
ax.set_ylim3d(-2, 2)
ax.set_zlim3d(-2, 2)
ax.set_xlabel('x', fontsize=15, rotation=0)
ax.set_ylabel('y', fontsize=15, rotation=0)
ax.set_zlabel('z', fontsize=15, rotation=90)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks([0,np.pi,2*np.pi,3*np.pi,4*np.pi])
ax.set_xticklabels([0,'$\pi$','2$\pi$','3$\pi$','4$\pi$'])
ax.yaxis.set_ticks([-2,-1,0,1,2])
ax.zaxis.set_ticks([-2,-1,0,1,2])
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
|
Turn Off Axis, Axis Labels, Grid
|
Filename : Line3D.py
|
|
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.axes3d as axes3d
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1, projection='3d')
t = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, 100)
x = t
y = np.cos(t)
z = np.sin(t)
ax.plot(x, y, z,'b')
ax.set_xlim3d(0, t.max())
ax.set_ylim3d(-2, 2)
ax.set_zlim3d(-2, 2)
ax.set_xlabel('x', fontsize=15, rotation=0)
ax.set_ylabel('y', fontsize=15, rotation=0)
ax.set_zlabel('z', fontsize=15, rotation=90)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks([0,np.pi,2*np.pi,3*np.pi,4*np.pi])
ax.set_xticklabels([0,'$\pi$','2$\pi$','3$\pi$','4$\pi$'])
ax.yaxis.set_ticks([-2,-1,0,1,2])
ax.zaxis.set_ticks([-2,-1,0,1,2])
ax.grid(False)
ax.axis('off')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_zticks([])
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|

|
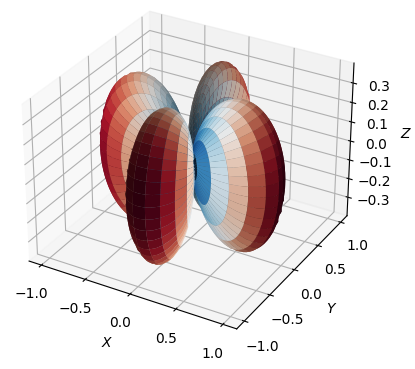
Color map
For most of 3D surface plot, you may not need to worry much about the colormap because the default color map would be good enough unless you have any specific preferance of your own. However for the 3D surface plot in spherical coordinate you may want to apply different colormap. In default colormap in 3d surface plot, the surface color changes as the value in Z axis varies, but in spherical plot it would be more meaning to change color of the surface as the value in Radial axis varies. This is an example of showing the color variation along with radial axis (not along with Z axis).
cmap in Spherical Coordinate
|
Filename : plot3d_spherical_color_01.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
# Generate spherical coordinates
phi = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 100)
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
PHI, THETA = np.meshgrid(phi, theta)
R = (np.sin(PHI) ** 2) * np.cos(2 * THETA)
# Convert spherical coordinates to cartesian coordinates
X = R * np.sin(PHI) * np.cos(THETA)
Y = R * np.sin(PHI) * np.sin(THETA)
Z = R * np.cos(PHI)
# Normalize r for color encoding
normalized_r = np.abs(R)
normalized_r = (normalized_r - normalized_r.min()) / (normalized_r.max() - normalized_r.min())
# Define a colormap that maps normalized r to red or blue
cmap = cm.get_cmap('RdBu_r')
colors = cmap(normalized_r)
# Plot the surface
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, facecolors=colors, linewidth=0)
ax.set_xlabel(r'$X$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'$Y$')
ax.set_zlabel(r'$Z$')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
|
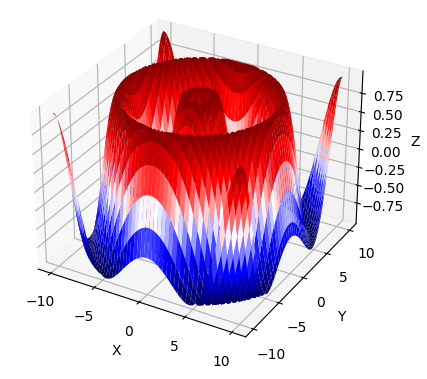
cmap in Cartesian Coordinate
If you apply the color map to cartesian surface plot, it become a little bit simple as below.
|
Filename : plot3d_surce_01_cmap.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# create custom colormap
cmap = plt.cm.get_cmap('seismic')
# plot surface using custom colormap
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cmap)
# add labels and show the plot
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
|
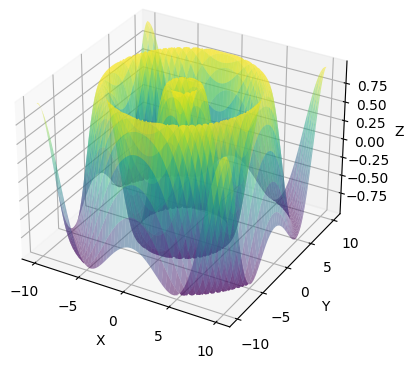
Setting Transparency
If you can change transparency of the surface color as shown below.
|
Filename : plot3d_surce_01_cmap.py
|
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate some sample data
X, Y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-10, 10, 100), np.linspace(-10, 10, 100))
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# create the plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# plot surface with transparency
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap='viridis', alpha=0.5)
# add labels and show the plot
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
|
| Result : |
|
|
Reference :
[1] Matplotlib tutorial (Nicolas P. Rougier)
|
|












