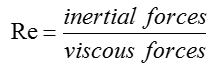|
Mechanical Engineering |
||
|
Fluid Mechanics : Reynolds Number
When a fluid flow through a certain path, a specific flow pattern forms depending on various factors. Reynold number is a special indicator that represents the flow pattern in a specific number.
A high level definition of Reynolds Number is described as follows. As you can see from this equation, Reynalds Number represents the ratio of inertial forces and viscous forces of a fluid. As inertial forces increases, Reynolds number descreases and as viscous forces increases, Reynolds number decreases.
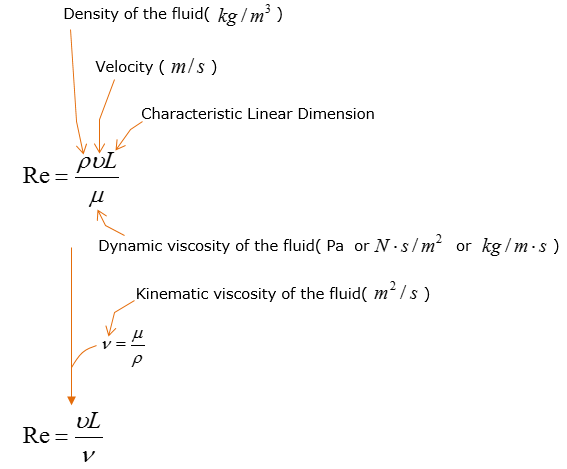
Reynolds number can be described in a form showing more specific properties of the fluid and physical dimension of the path the fluid flow through.
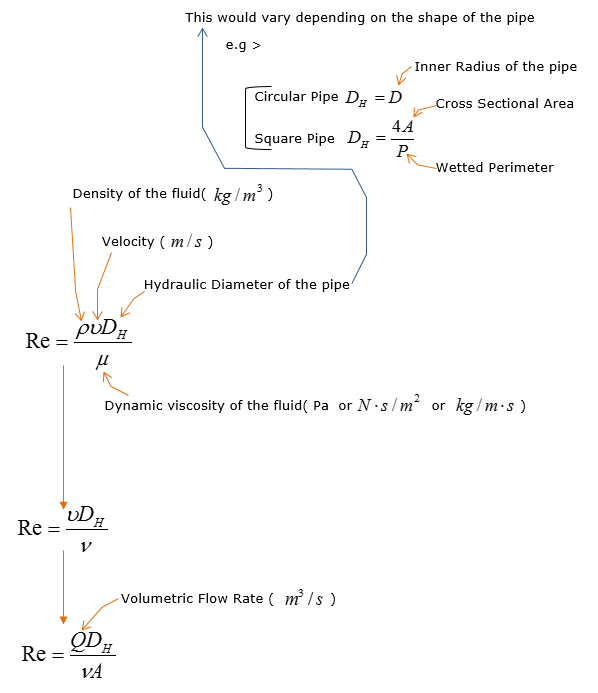
You would understand that you would be able to get the most of the parameters used in in the above equation from characteristics of the fluid itself. But what does 'L (Characteristic Linear Dimension)' really mean ? The term(parameter) L is not the characteristics of the fulid itself, it is the characteristics of the path through which the fluid flow. For example, if the path is a kind of Pipe. The term 'L' can be expressed as D(H) and the Raynolds number equation can be re-written as follows.
Reynolds number are used on it's own to represents a flow pattern of a fluid or it is also widely used to estimate Friction factor from Moody's diagram.
Reference :
[1] Reynolds Number - Sixty Symbols [2] Reynolds Numbers and Turbulence (Fluid Mechanics - Lesson 11)
|
||