|
Switch
What would happen when a Packit comes into a switch port ?
When a packet comes into a switch port, a sequence of procedures would happen before it gets out of out of the switch. The procedure can be classified into roughly two cases as below.
When the incoming packet does not have VLAN information
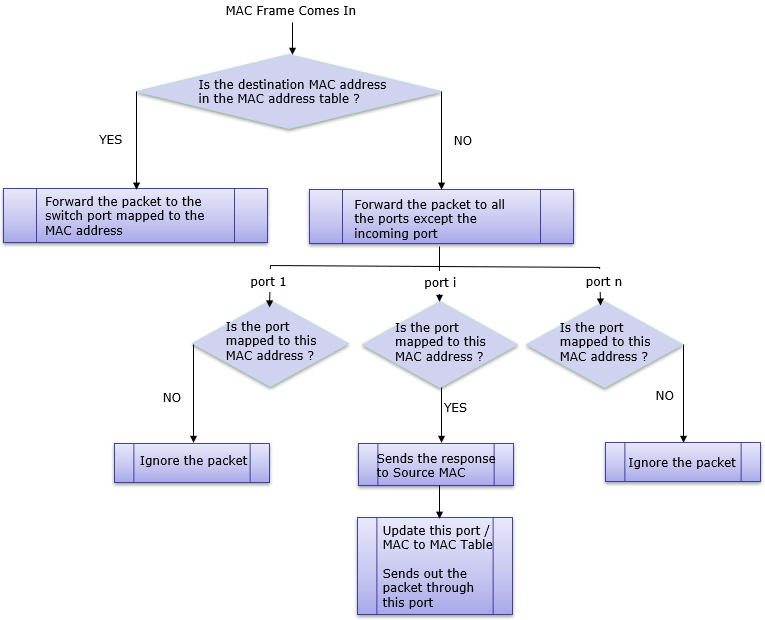
- Step 1 : A device sends an Ethernet frame to a switch without a VLAN tag.
- Step 2 : The switch examines the frame's destination MAC address to determine which port to send the frame out of. If the destination MAC address is not known, the switch does not have the necessary information to forward the frame to the correct port.
- Step 3 : The switch floods the frame out of all ports except the one it came in on, in an attempt to ensure that the frame reaches its destination.
- Step 4 : All devices connected to the switch receive the frame, including the device with the correct MAC address.
- Step 5 : The device with the correct MAC address responds to the frame.
- Step 6 : The switch learns the MAC address of the responding device and updates its internal MAC address table accordingly, associating the MAC address with the port the frame was received on.
- Step 7 : The next time the switch receives a frame addressed to the same MAC address, it will forward it out of the appropriate port, without any flooding.
When the incoming packet has VLAN information
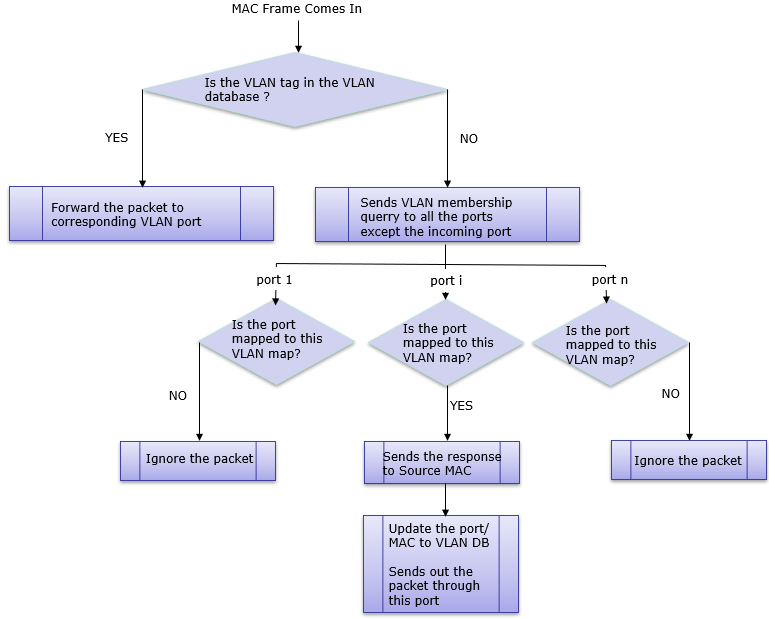
NOTE : Regarding the details of VLAN concept, check out the note on VLAN.
Reference
|
|



