|
BCI(Brain Computer Interface) / BMI (Brain Machine Interface)
BCI refers to Brain Computer Interface and some people likes to call it as Brain Machine Interface. Since computer can get connected to so many other machines and control them easily, once your brain get connected to a computer it can get the control over almost everything outside of your body.
The concept itself is simple. It is connecting brain to computer or machine as illustrated below. The question is 'HOW'.
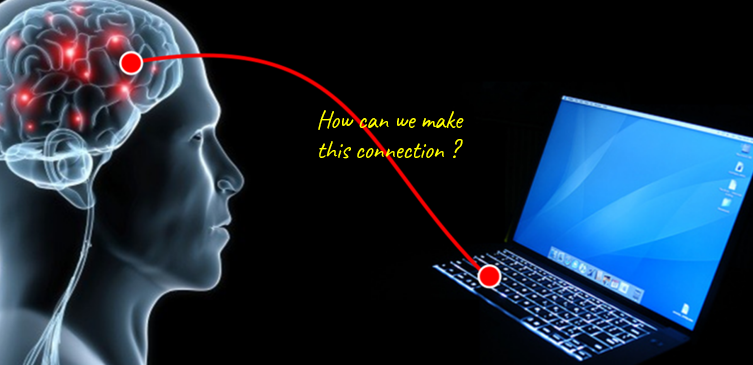
Image Source : Bringing Brain Computer Interfaces Home
What I want to talk about BCI in this note are as follows :
It depends on how you define Science Fiction... but I think I know what you mean. There is no clear answer to this for now. Even among those players in the industry or academia of this field, some people sound like 'it is real' but some other people say 'it is far, far away from reality' (even though they would not say 'science fiction' explicitely).
My personal opinion about this question are as follows (as of writing this. Dec 2022)
- It is real in terms of the facts that a lot of real research / experiments has been there for a long time
- The first attempt to manipulate something on computer (e.g, moving cursor on computer) can trace back to as early as early 1970's.
- I think (I think I should admit) that this field has attracted the widest attention out of general public since Neralink started promoting their activities (around 2020)
- In terms of what the academia and industry really achieved, it seems promising but still far away from what they claim as final goal.
- I would suggest the readers to pay more attention to what they realy achieved and published as data (e.g, academic paper or at least real demonstration) than what they claim would be possible in the future. It would be possible 'THE FUTURE' can be very far.
Why BCI ? Why do we want to create this kind of interface ? There are wide range of motivation for BCI and some of most frequently motivations are as follows :
- Restore or improve function : It can help people with severe motor impairments, such as those with spinal cord injuries or Lou Gehrig's disease (ALS), to communicate or control their environment. ==> I think this may
be the strongest motivation for most of the players in the industry. At least, most of those players seems to claim that this is one ther main goal.
- Enhance human performance : It can improve sensory and cognitive functions, such as perception, attention, and memory, which could have applications in a range of fields, including military, sports, and entertainment ==>
One of the early sponsors for BCI was DARPA and I guess (but not for sure) they were more motivated for this purpose.
- Facilitate research to advance our understanding of the brain : It can be used to study brain function and how it changes over time, as well as to investigate the effects of brain disorders or injuries and these research can can provide insights into how the brain processes information and can be used
to develop new theories about brain function
There are roughly two different types of connecting the brain to computer. One is called Invasive method and the other one is called Noninvasive method.
Invasive Method: This is the method / technology that requires physical break-open to look into a system. In terms of BCI, it is the method that requires physical operation to connect the brain to computer. Most of BCI technology except EEG belongs to this category.
NonInvasive Method: This is the method / technology that does not requires physical break-open to look into a system. In terms of BCI, it is the method that does not requires physical operation to connect the brain to computer. EEG is the most typical example of Noninvasive technology.
It would sound fancy to make connection between brain and computer/machine and control everything with your brain, but you know the reality never goes like textbook. It is not easy to realize the connection. With all sort of challenges, there has still been various attempts and prototypes. In this section, I am going to list well known (at least well known to me) examples of physical
interface between brain and computer/machine.
EEG stands for ElectroEncephaloGram. This would be the most widely used and safest interface. This is non-invasive technology. Just sticking bunch of electrode on top of the brain as shown below and reads electrical signals from each of the electrodes. This technology has been used for long time in diagnosis or other brain researches not associated with BCI.
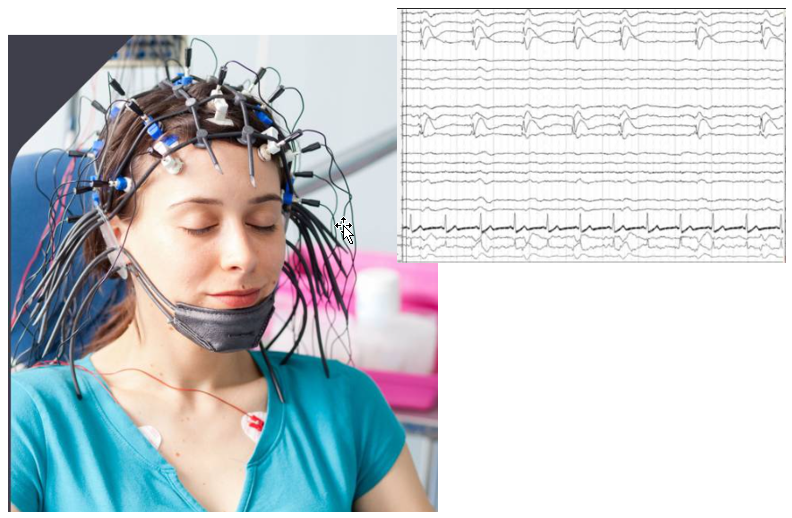
Once you got these electrode connected and you need to have proper software algorithm to analyze those signals to associate with specific activities (e.g, moving a mouse pointer, pressing a specific key on virtual keyboard etc). Usually various AI algorithms are used for this purpose.
The Utah Electrode Array(UEA) is an arry of electrode that is designed to inserted into a specific brain region and recorde the activity of multiple layers of the cortex area simultenously (For the details of electrode itself, check out this note) . As the name implies it was developed at the University
of Utah, and it has been used in a variety of research and clinical applications. It was aimed at developing a brain-machine interface that could be used to control prosthetic devices, such as a robotic arm or a computer cursor, using the activity of neurons in the brain. The UEA has since been widely used in research and clinical settings, and has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the brain and the development of treatments for neurological disorders.
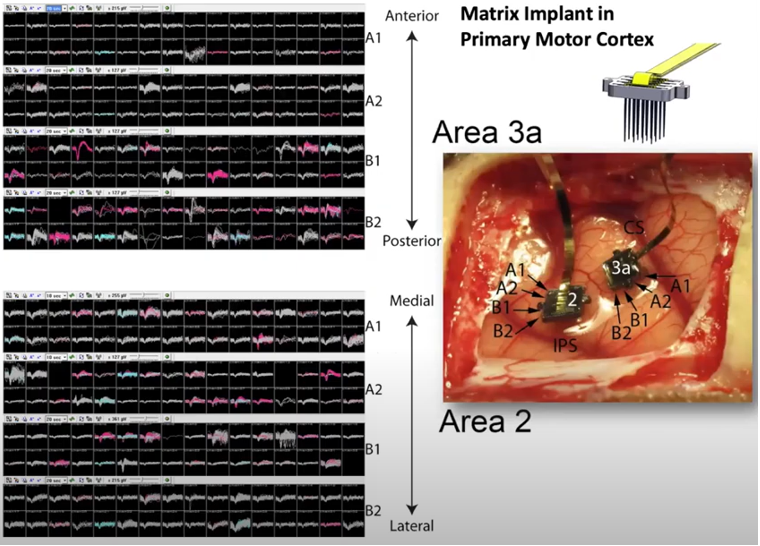
Image Source : Electrode Technology with Dr. Rio Vetter | Webinar
Stentrode is a term coined by combining two words : Stents and Electrode. Stents is a small mesh of metals that has been develop to treat narrow or weak blood vessels. Since it was developed in 1970s, it has widely used in the field. The idea behind the strentrode is to attach electrodes in the stents and place it within a blood vessel which are closes to the brain part that we want to
interact (i.e, reading the electric activity of the brain part). The other end of the stentrode located outside of the body and wirelessly connected to computer.
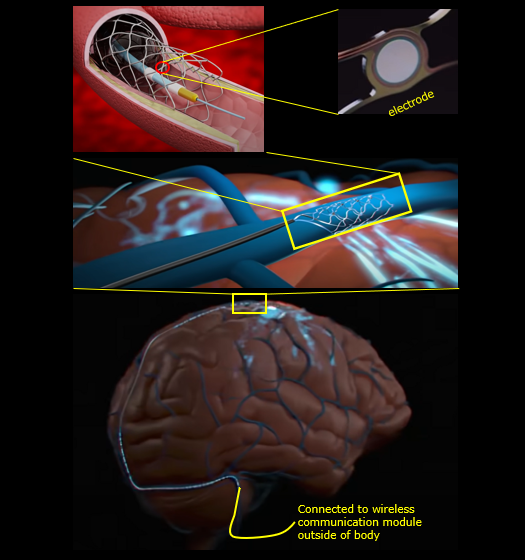
Image Source : A Brain Implant That Turns Your Thoughts Into Text | Tom Oxley | TED
Understadably this would record better the electrical activity of a brain part comparing to EEG beause the electrode is placed closer to the brain region comparing EEG, but may not record at the same level of sensitivity / accuracy as Utha electrode or Neuralink since the stentrode cannot get as close to the brain region as Utha electrode or Neuralink thread.
I think the biggest advantage of the stentroid is that it may achieve great tradeoff between signal accuracy and safety. In terms of signal accuracy, it may not be as accurate / sensitive as Utha electrode or Neuralink thread but it is based on the technology (stents) that has been proved safe for long time.
Neuralink, founded by Elon Musk and a team of leading scientists and engineers, is a neurotechnology company pioneering the development of brain-machine interfaces (BMIs). Their groundbreaking work centers on creating implantable devices that can seamlessly connect the human brain with computers, aiming to enhance human capabilities, treat neurological disorders, and ultimately merge human consciousness with artificial intelligence. Neuralink's innovative approach, combining cutting-edge neuroscience, miniaturized electronics, and advanced surgical techniques, has the potential to revolutionize how we interact with technology and understand the complexities of the human brain.
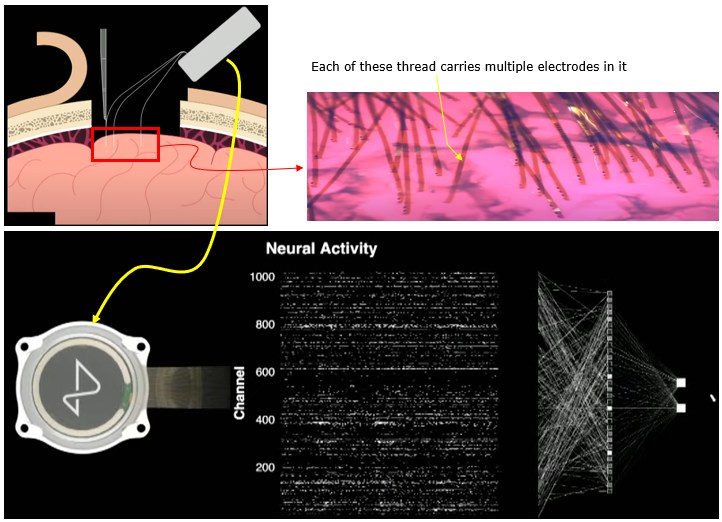
Image Source : Neuralink Show and Tell, Fall 2022
NOTE : For the location of Neurolink chip and the functionality of the region, refer to this note.
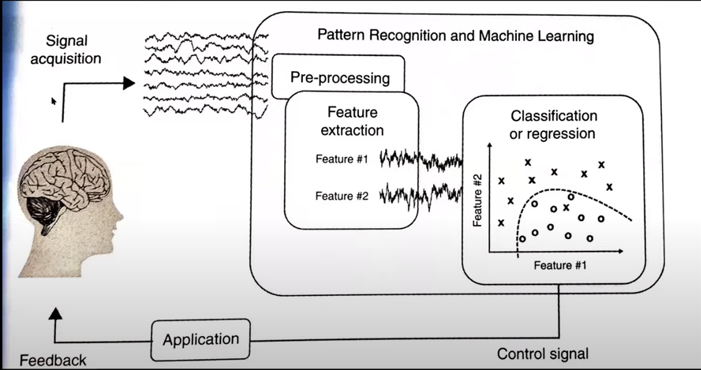
Main goal of BCI is to collect the various information(signal) from brain as accurately as possible and to best translate them into intended actions. This is super difficult technology and will be on-going forever, but a sequence of general approach can be summarized as follows.
- Signal Acquisition: The first step is to acquire the brain signals, typically using methods like EEG (electroencephalography), MEG (magnetoencephalography), or fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging). EEG is the most common for BCIs due to its non-invasiveness and relatively low cost.
- Preprocessing: This step involves cleaning the acquired signal. Brain signals are often contaminated with noise and artifacts from various sources like muscle movements (EMG), eye blinks (EOG), or external environmental factors. Techniques like band-pass filtering, artifact rejection algorithms, and independent component analysis (ICA) are used to reduce
these unwanted signals.
- Feature Extraction: Here, the goal is to identify and extract features from the EEG signals that are most relevant to the intended action. These features could be in the time domain, frequency domain, or time-frequency domain. Commonly used features include power spectral density, wavelet transform coefficients, and event-related potentials (ERPs).
- Classification or Regression: After extracting the features, the next step is to use machine learning algorithms to classify the signals into different categories (e.g., intended actions vs non-intended) or to perform regression analysis for continuous control. Algorithms like support vector machines (SVM), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), neural
networks, or deep learning models are typically employed.
- Training and Calibration: This involves training the BCI system with the user's specific brain patterns. The user is asked to perform or imagine the intended actions several times to allow the system to learn the corresponding brain signal patterns.
- Real-Time Processing and Feedback: In real-time BCI applications, the system processes incoming brain signals, classifies them into intended actions or non-actions, and translates them into outputs (e.g., moving a cursor or a robotic arm). Providing real-time feedback to the user is crucial for improving the system's accuracy and the user's control over
the BCI.
- Adaptation and Learning: Over time, both the user and the BCI system can adapt to each other. The user might learn to generate clearer signal patterns, while the system can continuously update its models to improve accuracy
There are many BCI technologies as shown above (there would be even more that are not introduced in this note), but at least as of now (as of writing this note : Jan 2023) it doesn't seem that there is any best solutions. Each of the technologies appears to have its own challenges. I am trying to list some of challenges that are mentioned most commonly.
In terms of safety, Noninvasive technology like EEG would be almost ideal (seemily no known harms), but there would be some challenges listed below. The first 5 items are what I got from chatting with chatGPT and I agree with the reply from it. It is an amazing that I can chat with an AI about this kind of topics and at this kind kind of level (human like response).
- Low signal-to-noise ratio: The brain's electric signals are very weak and are easily drowned out by noise from other sources such as muscle activity, eye movements, and electrical interference. This makes it difficult to accurately detect and interpret the brain's signals.
- Limited spatial resolution: EEG can only measure the brain's activity at a relatively coarse scale, as the electrodes are typically placed on the scalp. This means that it is difficult to accurately localize the source of the brain's activity to specific regions or circuits within the brain.
- Limited temporal resolution: EEG has a relatively slow temporal resolution compared to other techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), making it difficult to track rapid changes in brain activity.
- User-dependent variability: The EEG signals can vary significantly between individuals, and even within the same individual on different days. This makes it difficult to develop BCI systems that are robust and reliable across different users.
- Limited application domain: The current state of EEG-based BCI technology is limited to simple control tasks such as moving a cursor on a screen or controlling a prosthetic limb. It is not yet practical for more complex tasks such as natural language communication or multitasking.
- Physical Connection Difficulties: It would be cumbersome to connect all those electrode onto brain everytime you want to measure the signal. Even though we are seeing more and more examples of handy EEG recording devices (like helmet or band type), I think it is still combersome to set this up everytime.
It would not be put those electrode at exactly same position when we take off and put on again.
- Read Only: As far as I know, I see EEG being used only for recording brain signal and I haven't see any case where it can be used to stimulate a specific brain area.
Invasive technology such as Utah Electrode Array, Nuralink, Stentrode etc surpass better than non-invasive technology (e.g, EEG) in terms of signal strength, spatial / temporal resolution etc. But these technology have their own challenges as well. Some of these challenges are listed below. The first 5 items are what I got from chatting with chatGPT and I agree with the reply from it.
- Risk of infection: Surgical procedures carry a risk of infection, which can be serious if it occurs in the brain.
- Risk of brain damage: There is also a risk of damaging the brain or causing other complications during the surgical implantation of the electrodes.
- Limited long-term stability: Implanted electrodes can shift or become displaced over time, which can affect the quality of the signal being recorded. They may also suffer from a gradual decline in performance, requiring replacement or repair.
- Ethical concerns: The use of invasive BCI technologies raises ethical concerns, as they involve a permanent alteration to an individual's body and may have unknown long-term effects.
- Cost and accessibility: Invasive BCI technologies are typically more expensive and require specialized surgical procedures, which may limit their accessibility.
- Risk of damaging Blood Vessels: Even if the damage is not as serious as to be called brain damage, there is still risk of damaging many of small blood vessels when implanting the electrode into the cortex of the brain. In case of Neralink, they claim that the blood vessel implaning machine (robot)
has capability of recognizing all the blood vessel and avoiding the vessel when it implanting the thread(electrode), but it is still in debate on accuracy and reliability of the robot operation.
- Coping with Brain Pulsation: You may think the brain is a stationary (i.e, not moving) organ sitting within the skull, but in reality it moves (at least the surface of the brain) constantly. It pulses like heart. Of course, it does not strongly pulses in wide range as heart, but it pulses. If you implant electrode into the brain, you need
to understand how the implanted electrode is affected by such a movement and check whether the electrode cause any long term damage due to the movement.
Regardless of whether they use Invasive technology or non Invasive technology, it is highly likely that the interfacing between the electrode and computer/machine would be based on wireless communication when it is commercialized for public. When the connection become wireless, they would come across some additional challenges. Some of the widely mentioned challenges with wireless communication
are listed as below.
- Limited Bandwidth:
- Battery/Energy Consumption:
- Difficulties in Charging:
Prosthetics are devices that are used to replace or enhance a missing or impaired body part. The field of prosthetics is focused on designing, developing, and fitting these devices to help people with physical limitations to improve their mobility, function, and quality of life.
Prosthetics can be classified into two main categories: external prosthetics, which are worn on the outside of the body, and internal prosthetics, which are implanted inside the body.
- Examples of External prosthetics:
- Amputation Prosthetics which are used to replace limbs that have been lost due to injury or disease. They include devices such as artificial arms and legs, which can be controlled by the user's remaining muscles and nerves.
- Orthotic devices which are used to support or align weak or deformed body parts, such as braces for the back or legs.
- Assistive devices which are used to help people with mobility, such as crutches, walkers, and wheelchairs.
- Examples of Internal prosthetics:
- Cochlear implants which are used to help people with hearing loss by electrically stimulating the auditory nerve.
- Retinal implants which are used to help people with vision loss by electrically stimulating the retina.
- Artificial heart valves which are used to replace damaged or diseased heart valves.
Reference
YouTube
- EEG
- Utah Electrode Array
- Stents Electrode (Stentrode)
- Neurobypass
- Neuralink
- General
- Misc
|
|





