|
Matlab/Octave |
|||||||||
|
CSV File Manipulation
Examples of CSV Writing
Examples of CSV Reading
CSV Writing
Example 1 : Writing a real number pairs with csvwrite()
t = 0:pi/10:2*pi; y = sin(t);
csvwrite('sin_t.dat',[t;y]');
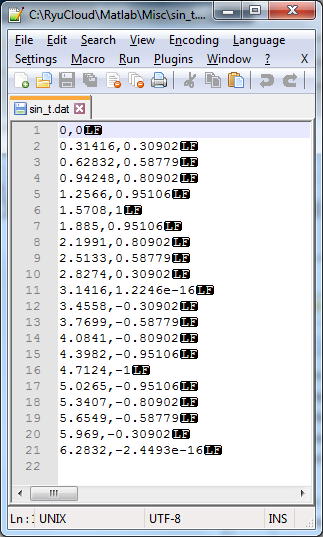
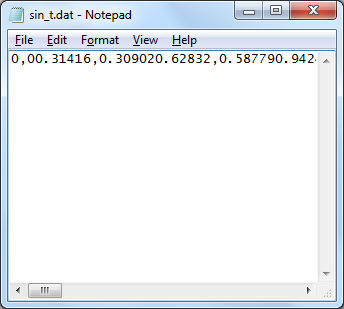
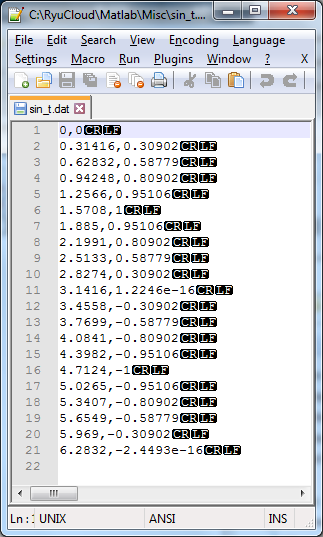
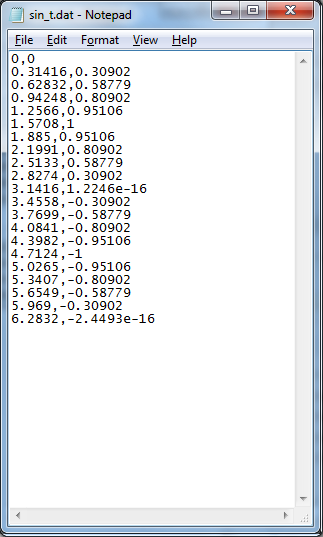
csvwrite saves the data and put only LineFeed character at the end of each line. So if you open the csv file in Note++, Excell, Word , you will see the data as shown on the left (this is what you expected), but if you read the file with NotePad, you would see the contents as shown on right. This is because Notepad does not change the line only with LineFeed character. You need to put both Carriage Return character and Line Feed character at the end of the line. However, csvwrite() does not have any options to specify the end of line format. In this case, you need to use dlmwrite() as in the next example.
Example 2 : Writing a real number pairs with dlmwrite()
dlmwrite() function do similar function as csvwrite(), but it can specify various additional options like 'newline' or 'delimiter' etc. t = 0:pi/10:2*pi; y = sin(t);
data = [t;y]';
dlmwrite('sin_t.dat',data,'newline','pc');
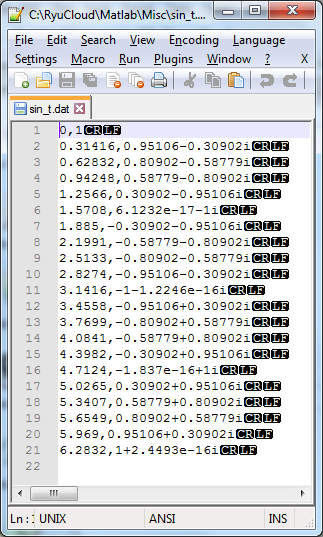
Example 3 : Writing a complex number pairs with dlmwrite()
t = 0:pi/10:2*pi; y = exp(i*t);
data = [t;y]';
dlmwrite('sin_t.dat',data,'newline','pc');
Example 4 : Writing a number with dlmwrite() in a specific numeric precision
t = 0:pi/10:2*pi; y = exp(i*t);
data = [t;y]';
dlmwrite('sin_t.dat',data,'newline','pc','precision',6);
CSV Reading
Example 1 : Reading a real number pair
This example is to read a data as shown below.
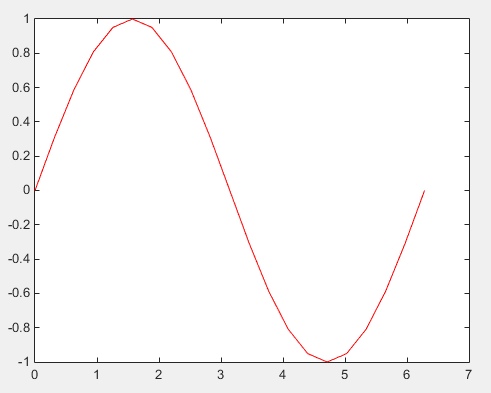
data = csvread('sin_t.dat'); plot(data(:,1),data(:,2),'r-');
Following is the result.
Example 2 : Reading a data with complex numbers
This example is to read a data as shown below.
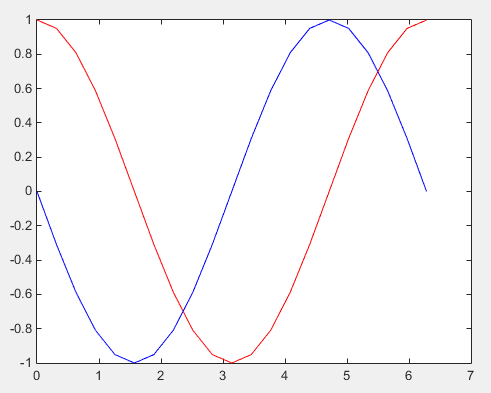
data = csvread('complex.dat'); plot(data(:,1),real(data(:,2)),'r-',data(:,1),imag(data(:,2)),'b-'); Following is the result.
|
|||||||||