|
Service Setup
The Service Request procedure in 5G is used when a device wants to establish a connection to the AMF. There are two possible scenarios in which this can happen: Network Triggered and UE Triggered Request. In practice, I think UE triggered Request is more common.
In more formal expression as stated in 24.501-5.6.1.1, 'The purpose of the service request procedure is to change the 5GMM mode from 5GMM-IDLE to 5GMMCONNECTED mode.' as highlighted in the following statemachine.
< 24.501 Figure 5.1.3.2.1.1.1: 5GMM main states in the UE >
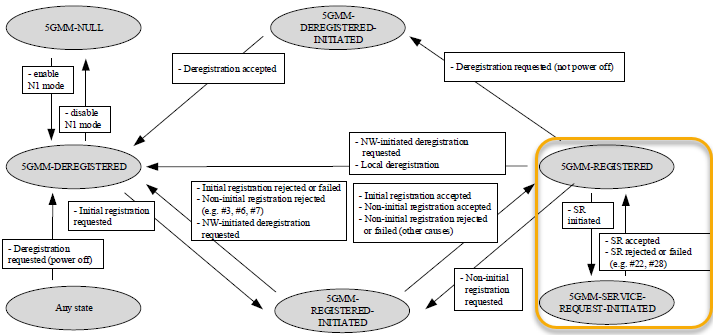
In this note, I will talk about the details of Service Request procedure as follows.
When UE is supposed to trigger Service Request ? The most common case is when there is some data to be sent by UE while it is in idle mode, UE initiate the service request.
More detailed case description for UE initiated Service Request is stated in 24.501-5.6.1.1 as follows : (NOTE : The first two cases would be the most common cases you would see in regular operations)
- the UE has uplink signalling pending over 3GPP access and the UE is in 5GMM-IDLE mode over 3GPP access
- the UE has user data pending over 3GPP access and the UE is in 5GMM-IDLE or 5GMM-CONNECTED mode over 3GPP access;
- the UE has user data pending over non-3GPP access and the UE is in 5GMM-CONNECTED mode over non-3GPP access;
- the UE in 5GMM-IDLE mode over non-3GPP access, receives an indication from the lower layers of non-3GPP access, that the access stratum connection is established between UE and network, if T3346 is not running;
- the UE in 5GMM-IDLE or 5GMM-CONNECTED mode over 3GPP access receives a request from the upper layers to perform emergency service fallback and performs emergency services fallback
- the UE has to request resources for V2X communication over PC5.
When UE is supposed to trigger Service Request ? The most common case is when there is some data to be sent by Network while it is in idle mode, NW(Network) initiate the service request.
More detailed case description for NW initiated Service Request is stated in 24.501-5.6.1.1 as follows : (NOTE : The first two cases would be the most common cases you would see in regular operations)
- the network has downlink signalling pending over 3GPP access and the UE is in 5GMM-IDLE mode over 3GPP access;
- the network has downlink user data pending over 3GPP access and the UE is in 5GMM-IDLE mode over 3GPP access;
- the network has downlink signalling pending over non-3GPP access, the UE is in 5GMM-IDLE mode over non- 3GPP access and in 5GMM-IDLE or 5GMM-CONNECTED mode over 3GPP access
- the network has downlink user data pending over non-3GPP access, the UE is in 5GMM-IDLE mode over non-3GPP access and in 5GMM-IDLE or 5GMM-CONNECTED mode over 3GPP access
According to 24.501 - 5.6.1.1 Service Setup procedure initiation goes as follows.
< Case A > Normal Service Setup
|
Direction
|
Message
|
UE Timer
|
NW Timer
|
|
UE -> NW(AMF)
|
SERVICE REQUEST
|
T3517 Start
|
|
|
UE <- NW(AMF)
|
SERVICE ACCEPT
|
T3517 Stop
|
|
< Case B > No Service Accept
|
Direction
|
Message
|
UE Timer
|
NW Timer
|
|
UE -> NW(AMF)
|
SERVICE REQUEST
|
T3517 Start
|
|
|
UE <- NW(AMF)
|
No SERVICE ACCEPT
|
T3517 Expire
|
|
< Case C > Service Reject
|
Direction
|
Message
|
UE Timer
|
NW Timer
|
|
UE -> NW(AMF)
|
SERVICE REQUEST
|
T3517 Start
|
|
|
UE <- NW(AMF)
|
SERVICE REJECT
|
T3517 Stop
|
|
Following is a table listing various reject cause and the expected UE behavior based on 24.501-5.6.1.5 and 24.501-AnnexA. I put only high level and most critical (most critical to me) in the 'Expected UE behavior' column. There are much more futher details specified in the specification.
|
Reject Cause
|
Expected UE Behavior
|
|
#3 (Illegal UE); or
#6 (Illegal ME).
|
- The UE shall consider the USIM as invalid for 5GS services until switching off or the UICC containing the USIM is removed
|
|
#7 (5GS services not allowed)
|
- The UE shall consider the USIM as invalid for 5GS services until switching off or the UICC containing the USIM is removed
|
|
#9 (UE identity cannot be derived by the network)
|
- The UE shall set the 5GS update status to 5U2 NOT UPDATED (and shall store it) and shall delete any 5G-GUTI, last visited registered TAI, TAI list and ngKSI. The UE shall enter the state 5GMM-DEREGISTERED.
- If the service request was initiated for emergency services fallback, the UE shall attempt to select an E-UTRA cell connected to EPC or 5GCN according to the domain priority and selection rules specified in 23.167. If the UE finds a suitable E-UTRA cell, it then proceeds with the appropriate EMM or 5GMM procedures.
- If the service request was initiated for any reason other than emergency services fallback or initiating an emergency PDU session, the UE shall perform a new initial registration procedure
|
|
#10 (Implicitly de-registered)
|
- The UE shall enter the state 5GMM-DEREGISTERED.NORMAL-SERVICE. The UE shall delete any mapped 5G NAS security context or partial native 5G NAS security context.
- If the rejected request was not for initiating an emergency PDU session, the UE shall perform a new initial registration procedure.
|
|
#11 (PLMN not allowed)
|
- The UE shall delete the list of equivalent PLMNs and store the PLMN identity in the "forbidden PLMN list". The UE shall enter the state 5GMM-DEREGISTERED and perform a PLMN selection
|
|
#12 (Tracking area not allowed)
|
- The UE shall set the 5GS update status to 5U3 ROAMING NOT ALLOWED and shall delete 5G-GUTI, last visited registered TAI, TAI list and ngKSI.
- The UE shall store the current TAI in the list of "5GS forbidden tracking areas for regional provision of service" and enter the state 5GMM-DEREGISTERED.LIMITED-SERVICE.
|
|
#13 (Roaming not allowed in this tracking area)
|
- The UE shall enter the state 5GMM-REGISTERED.PLMN-SEARCH.
- The UE shall store the current TAI in the list of "5GS forbidden tracking areas for roaming" and remove the current TAI from the stored TAI list if present.
- The UE shall perform a PLMN selection.
|
|
#15 (No suitable cells in tracking area)
|
- The UE shall enter the state 5GMM-REGISTERED.LIMITED-SERVICE.
- The UE shall store the current TAI in the list of "5GS forbidden tracking areas for roaming" and remove the current TAI from the stored TAI list if present.
- If the service request was not initiated for emergency services fallback, the UE shall search for a suitable cell in another tracking area.
|
|
#22 (Congestion)
|
- If the T3346 value IE is present in the SERVICE REJECT message and the value indicates that this timer is neither zero nor deactivated, the UE shall proceed as described below
- If the rejected request was not for initiating an emergency PDU session, the UE shall abort the service request procedure and enter state 5GMM-REGISTERED, and stop timer T3517 if still running.
|
|
#27 (N1 mode not allowed)
|
- The UE shall disable the N1 mode capability for both 3GPP access and non-3GPP access
|
|
#28 (Restricted service area)
|
- UE shall perform the registration procedure for mobility and periodic registration update unless the service type IE in the SERVICE REQUEST message was set to "elevated signalling" .
- If the service type IE in the SERVICE REQUEST message was set to "elevated signalling", the UE shall not reinitiate service request procedure until the UE enters an allowed area or leaves a non-allowed area, except for emergency services, high priority access or responding to paging or notification.
|
|
#72 (Non-3GPP access to 5GCN not allowed)
|
- UE shall delete 5GGUTI,last visited registered TAI, TAI list and ngKSI for non-3GPP access. Additionally, the UE shall reset the registration attempt counter and enter the state 5GMM-DEREGISTERED for non-3GPP access.
- The UE shall disable the N1 mode capability for non-3GPP access
|
|
#73 (Serving network not authorized)
|
- The UE shall set the 5GS update status to 5U2 NOT UPDATED, store the PLMN identity in the "forbidden PLMN list" and enter state 5GMM-DEREGISTERED.PLMN-SEARCH in order to perform a PLMN selection
|
The structure of messages and a specific IE(Information Elements) involved in Service Setup process listed below :
The Service Request message is used when a UE in 5G idle/inactive state wants to resume service (to send/receive data or signaling). These IEs provide the network enough information to re-establish the UE’s context, security parameters, and PDU session status. The references (e.g., 24.501-9.11.3.x) point to exact sections in the 3GPP specification where each IE’s encoding and behavior are fully described.
Service Request (24.501-8.2.16.1)
Service request message identity (24.501-9.7)
ngKSI(24.501-9.11.3.32)
Service type(24.501-9.11.3.50)
5G-S-TMSI(24.501-9.11.33.4)
Uplink data status(24.501-9.11.3.57)
PDU session status(24.501-9.11.3.44)
Allowed PDU session status(24.501-9.11.3.13)
NAS message container(24.501-9.11.3.33)
Following is brief description on each of the IEs
- Service Request Message Identity
- A small, fixed code that identifies this NAS message as a “Service Request.” Every NAS message (e.g., Registration Request, Service Request, etc.) has a unique message identity defined in 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.7.
- ngKSI (NAS key set identifier)
- Identifies which security context the UE (User Equipment) is using. The UE and the 5G core use this identifier to ensure that the correct NAS security keys are applied to protect the message. Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.32.
- Indicates the security context (Key Set Identifier) used for authentication and encryption.
- Service Type
- Indicates the type of service the UE is requesting. Common service types include “Mobile-Terminated data,” “Mobile-Originated signaling,” etc., helping the network understand why the UE wants to resume or establish a connection. Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.50.
- 5G-S-TMSI
- The 5G System Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity, a temporary ID used to identify the UE within the 5G system. It’s allocated by the 5G core and helps preserve user privacy over the air. Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.4.
- Uplink Data Status
- Conveys which PDU sessions have pending data on the UE side. This tells the network that the UE has uplink traffic buffered and needs resources. Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.57.
- Indicates which PDU (Packet Data Unit) sessions have uplink data pending transmission. A bitmask where each bit corresponds to a PDU session ID (e.g., bit 0 = PDU session 1).
- PDU Session Status
- Lists active PDU sessions from the UE’s viewpoint, letting the network know which sessions the UE still considers active. Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.44.
- Bitmask indicating active sessions (e.g., bit 1 = PDU session 2 is active).
- Allowed PDU Session Status
- Tells the UE which of its requested or active PDU sessions the network is allowing in the current service request procedure (e.g., after a potential restriction). Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.13.
- NAS Message Container
- A container that can carry additional NAS messages or parameters if needed (often used for embedding secondary NAS messages or piggybacking procedures). Reference: 3GPP TS 24.501 § 9.11.3.33.
Example 01 >
This is a sample message from the log provided by Amarisoft. Highlights of this message is as follows.
- This message is triggered by the existence of pending data on UE (saying 'I have some data to send'). This is indicated by the IE 'Service Type'.
- The PSI (PDU Session Identifier) for the pending data (data to be sent) is 5. This is indicated by the IE 'uplink data status'
- The PSI (PDU Session Identifier) for the currently active PDU is 5. This is indicated by the IE 'PDU session status'.
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x1 (Integrity protected)
Auth code = 0x749766c9
Sequence number = 0x03
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x4c (Service request)
ngKSI:
TSC = 0
NAS key set identifier = 0
Service type = 0x01 (data)
5G-S-TMSI:
5G-S-TMSI
AMF Set ID = 4
AMF Pointer = 1
5G-TMSI = 0x82fbff80
NAS message container:
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x4c (Service request)
ngKSI:
TSC = 0
NAS key set identifier = 0
Service type = 0x01 (data)
5G-S-TMSI:
5G-S-TMSI
AMF Set ID = 4
AMF Pointer = 1
5G-TMSI = 0x82fbff80
Uplink data status:
0x20 (PSI(7)=0,PSI(6)=0,PSI(5)=1,PSI(4)=0,PSI(3)=0,PSI(2)=0,PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0,PSI(14)=0,PSI(13)=0,PSI(12)=0,PSI(11)=0,PSI(10)=0,PSI(9)=0,PSI(8)=0)
PDU session status:
0x20 (PSI(7)=0,PSI(6)=0,PSI(5)=1,PSI(4)=0,PSI(3)=0,PSI(2)=0,PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0,PSI(14)=0,PSI(13)=0,PSI(12)=0,PSI(11)=0,PSI(10)=0,PSI(9)=0,PSI(8)=0)
Following is the breakdown and description of the message
NAS Security Header & Protocol Discriminator
Outer NAS Header
----------------
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x1 (Integrity protected)
Auth code = 0x7a9766c9
Sequence number = 0x03
- Protocol discriminator (PD):
0x7e indicates a 5GS Mobility Management (5GMM) message.
- Security header = 0x1: Shows that the message is integrity-protected but not ciphered.
- Auth code: The integrity Message Authentication Code (MAC), ensuring message authenticity.
- Sequence number: Used to detect replay attacks and maintain message ordering.
Inner NAS Header (Plain)
------------------------
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x4c (Service Request)
- This is the Service Request message itself, encapsulated within an integrity-protected NAS header.
- The inner header (security header = 0x0) indicates it’s a plain (unencrypted) NAS message.
ngKSI
ngKSI:
TSC = 0
NAS key set identifier = 0
- TSC (Type of Security Context):
0 means a native 5G security context (as opposed to one mapped from LTE).
- NAS key set identifier: Tells the network which set of NAS security keys to use (here,
0).
Service Type
Service type = 0x01 (data)
- Service type = 0x01 (data): Indicates that the UE has mobile-originated data to send. This prompts the network to allocate or resume resources for data transfer.
5G-S-TMSI
5G-S-TMSI:
AMF Set ID = 4
AMF Pointer = 1
5G-TMSI = 0x82bf8ff80
- 5G-S-TMSI: A temporary identifier assigned to the UE by the AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function). It includes:
- AMF Set ID & AMF Pointer: Indicate which AMF instance allocated this TMSI.
- 5G-TMSI: The main temporary mobile subscriber identifier part.
NAS Message Container
NAS message container:
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message)
Message type = 0x4c (Service Request)
This field can encapsulate additional NAS messages or related information. It’s commonly seen in logs where certain procedures are “piggybacked” or re-encapsulated for completeness.
Uplink Data Status
Uplink data status:
0x20 (PSI(7)=0, PSI(6)=0, PSI(5)=1, PSI(4)=0, PSI(3)=0, PSI(2)=0, PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0, PSI(14)=0, PSI(13)=0, PSI(12)=0, PSI(11)=0, PSI(10)=0, PSI(9)=0, PSI(8)=0)
- This IE is a bitmap where each bit corresponds to a PDU Session ID (PSI).
- PSI(5) = 1 means the UE has uplink data waiting on PDU Session #5.
PDU Session Status
PDU session status:
0x20 (PSI(7)=0, PSI(6)=0, PSI(5)=1, PSI(4)=0, PSI(3)=0, PSI(2)=0, PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0, PSI(14)=0, PSI(13)=0, PSI(12)=0, PSI(11)=0, PSI(10)=0, PSI(9)=0, PSI(8)=0)
- Another bitmap indicating the UE’s currently active PDU sessions.
- PSI(5) = 1 confirms that PDU Session #5 is still active.
Service Accept is the NAS message the network sends to a UE in response to a Service Request. It tells the UE that its request was accepted and can also carry additional details about PDU sessions. It confirms that the UE can proceed with data transfer (for the active sessions) and indicates whether any sessions have been reactivated or encountered errors. If needed, it can also include an EAP payload for further authentication
Service Accept (24.501-8.2.17.1)
PDU session status(24.501-9.11.3.44)
PDU session reactivation result(24.501-9.11.3.42)
PDU session reactivation error cause(24.501-9.11.3.43)
EAP message(24.501-9.11.2.2)
Here are the key Information Elements (IEs) you typically see in a Service Accept:
- Service Accept Message Identity (24.501-9.7)
- A code that identifies this NAS message as a Service Accept.
- PDU Session Status (24.501-9.11.3.44)
- A bitmap telling the UE which of its PDU sessions are still active in the network’s view.
- For example, if the UE originally had multiple sessions open, this IE specifies which ones remain valid after the Service Accept.
- PDU Session Reactivation Result (24.501-9.11.3.42)
- Indicates which PDU sessions (if any) were successfully reactivated as part of resuming service.
- Typically used when the network tries to “wake up” sessions that were previously inactive or suspended.
- PDU Session Reactivation Error Cause (24.501-9.11.3.43)
- If any requested session reactivation failed, this IE provides the reason.
- Helps the UE determine why certain sessions were not reactivated (e.g., subscription restrictions, network conditions, etc.).
- EAP Message (24.501-9.11.2.2)
- Carries EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) data if the network requires additional authentication steps.
- This might appear during certain security procedures where EAP is used.
Example 01 >
This is a sample message from the log provided by Amarisoft.
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x2 (Integrity protected and ciphered)
Auth code = 0x91871bda
Sequence number = 0x04
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x4e (Service accept)
PDU session status:
0x20 (PSI(7)=0, PSI(6)=0, PSI(5)=1, PSI(4)=0, PSI(3)=0, PSI(2)=0, PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0,PSI(14)=0,PSI(13)=0,PSI(12)=0,PSI(11)=0,PSI(10)=0,PSI(9)=0,PSI(8)=0)
PDU session reactivation result:
0x00 (PSI(7)=0, PSI(6)=0, PSI(5)=0, PSI(4)=0, PSI(3)=0, PSI(2)=0, PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0,PSI(14)=0,PSI(13)=0,PSI(12)=0,PSI(11)=0,PSI(10)=0,PSI(9)=0,PSI(8)=0)
Below is a breakdown of the log fields in a 5G NAS Service Accept message.
Outer NAS Header
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x2 (Integrity protected & ciphered)
Auth code = 0x91871bda
Sequence number = 0x04
- Protocol discriminator (0x7e): Identifies this as a 5G Mobility Management (5GMM) NAS message.
- Security header = 0x2: The NAS message is both integrity-protected and ciphered.
- Auth code & Sequence number: Used for message authenticity and replay protection.
Inner NAS (Plain) Header
Protocol discriminator = 0x7e (5GS Mobility Management)
Security header = 0x0 (Plain 5GS NAS message, not security protected)
Message type = 0x4e (Service Accept)
- After decryption, the NAS message is revealed as a Service Accept (
0x4e).
PDU Session Status
0x20 (PSI(7)=0, PSI(6)=0, PSI(5)=1, PSI(4)=0, PSI(3)=0, PSI(2)=0, PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0, PSI(14)=0, PSI(13)=0, PSI(12)=0, PSI(11)=0, PSI(10)=0, PSI(9)=0, PSI(8)=0)
- This bitmap IE indicates which PDU sessions are active.
- PSI(5) = 1 means PDU Session #5 is currently active.
PDU Session Reactivation Result
0x00 (PSI(7)=0, PSI(6)=0, PSI(5)=0, PSI(4)=0, PSI(3)=0, PSI(2)=0, PSI(1)=0)
0x00 (PSI(15)=0, PSI(14)=0, PSI(13)=0, PSI(12)=0, PSI(11)=0, PSI(10)=0, PSI(9)=0, PSI(8)=0)
- This bitmap shows which PDU sessions (if any) were reactivated.
- All bits are
0, so there were no additional reactivations.
Service Type indicates the reason or context for the UE’s request to the network. It is included in certain 5G NAS messages (e.g., Service Request).
Service type value
signalling
data
mobile terminated services
emergency services
emergency services fallback
high priority access
elevated signalling
unused; shall be interpreted as "signalling", if received by the network
unused; shall be interpreted as "signalling", if received by the network
unused; shall be interpreted as "data", if received by the network
unused; shall be interpreted as "data", if received by the network
unused; shall be interpreted as "data", if received by the network
Service Type IEI
The standard defines the following Service Type values:
- Signalling
- The UE is requesting resources primarily to exchange signaling (e.g., NAS or RRC messages).
- Data
- The UE has user-plane data (e.g., IP traffic) to send or receive.
- Mobile Terminated Services
- The request is triggered by incoming traffic to the UE (e.g., a network-initiated service).
- Emergency Services
- The UE needs to establish a connection for emergency calls or sessions.
- Emergency Services Fallback
- Indicates a fallback scenario for emergency services (e.g., moving from 5G to LTE or other RAT if 5G coverage is insufficient).
- High Priority Access
- Used when the UE needs prioritized access (e.g., mission-critical or priority communications).
- Elevated Signalling
- Signaling with higher priority than normal (but not necessarily “emergency” or “high priority” data).
- Unused (interpreted as “signalling”)
- Some values are marked “unused” in the specification but, if received, the network treats them as equivalent to signalling.
- Unused (interpreted as “data”)
- Similarly, other unused values map to data if the network ever receives them.
Reference
Readings
|
|
